The best diet for hypothyroidism includes nutrient-rich foods like lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. It’s advisable to avoid or limit goitrogenic foods like cabbage and soy, and consider incorporating selenium-rich foods such as Brazil nuts. Consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized dietary advice.
What is Hypothyroidism?
It is known as hypothyroidism when the thyroid does not produce and transfer sufficient thyroid hormone into your blood [3]. In this condition, your metabolism gets slowed down, severely affecting your whole body. Hypothyroidism is also known as Myxedema [4]. Myxedema is the medical term that is used for abnormally low thyroid levels.
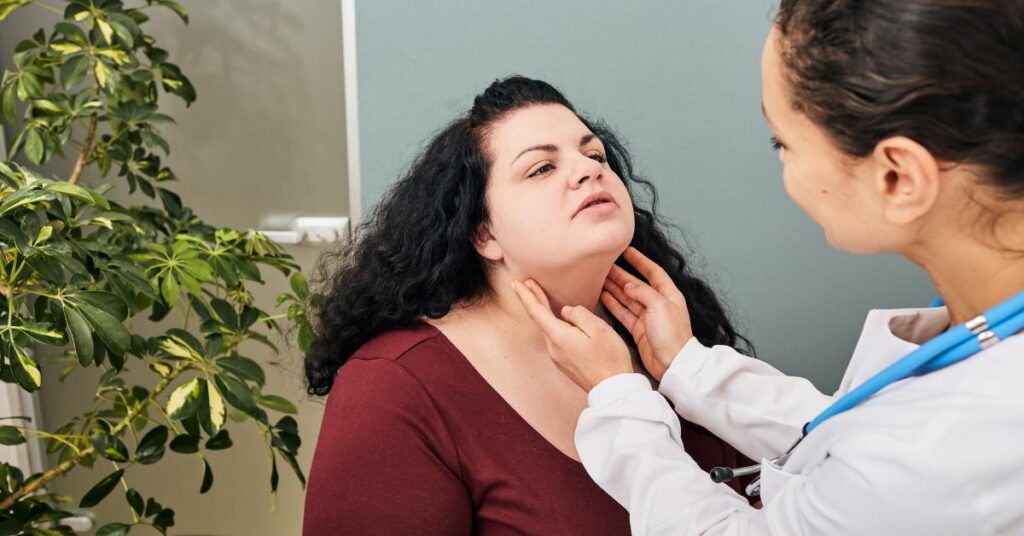

Metabolism, neurodevelopment, and cell repair are a few body processes regulated by thyroid hormones. In addition, hair loss, stomach pain, vomiting, weight gain, anxiety, cold, and memory loss are just a few common symptoms that hypothyroidism patients may experience [5].
What role does diet play?
Your diet plays an incredible role in your health. As it says, it takes 5 minutes to consume 500 calories and 2 hours to burn them off. So, you must better decide by yourself whether to eat well or experience problems in the future. The thyroid generates thyroid stimulating hormones TSH, which control a wide range of biological activities and helps maintain good health.
Therefore, a significant risk factor for thyroid illness is iodine deficiency. Due to the variety of foods available and each of them assumed to be the healthiest, it’s complicated. As a result, you must consume nutritious foods that will rebuild your bones and enhance your immune response.
Essential Nutrients for Thyroid Health
Thyroid hormone production and function depend on micronutrients, namely iodine, selenium [9], zinc, magnesium, iron, vitamin d, and b12. Iodine deficiency is regarded as the most frequent avoidable cause of goiters, thyroid cancer, and neurodevelopment worldwide since it is a necessary component of thyroid hormones.
Iodine
Iodine is a nutrient our body must consume daily, no matter what happens. Therefore, it is essential throughout pregnancy and the breastfeeding period for females. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of iodine in pregnant women is 220 micrograms per day.
For the good health of your thyroid, iodine is the most required nutrient [10]. Conversely, the most frequent cause of hypothyroidism is insufficient iodine supplements. Some of the unique advantages and benefits of iodine on human health are listed below:
- Thyroid promoting wellbeing
- Healthy growth throughout pregnancy
- Decrease in risk of Goiters
- Controlling an overactive thyroid
- Treats fibrocystic breast disease
- Thyroid cancer treatment
- Enhancing the mental ability
- Contaminating water
Defense against nuclear radiation

If you are suffering from hypothyroidism, you should not take iodine dietary supplements unless your doctor advises you to do so to address iodine deficiency.
Selenium
Selenium [11] is a vital mineral that you must consume in your diet. Selenium being a powerful antioxidative agent, lowers your chance of developing heart disease and maintains oxidative stress levels under control, which is good for your heart.
Selenium is only required in tiny amounts. Yet, it is vital for many bodily functions, such as the thyroid and metabolism. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of selenium in adults is 55 micrograms per day and for pregnant and lactating women is between 60-70 micrograms. Some significant benefits of selenium are listed below:
- Lowers chance of thyroid cancer
- Works as a barrier against heart disease.
- Powerful antioxidants.
- Promotes brain development
- Vital for the health of the thyroid.
- Decrease asthmatic symptoms
- Increase the body’s defense system.
Moreover, people with Alzheimer’s may benefit from a diet high in selenium since it may help improve brain development and memory loss.
Zinc
Zinc is a necessary mineral to perform various body functions and systems. Each cell in the body has zinc [12]. It is essential for the action of proteins, enzymes, and DNA and promotes cell and cell division development. Zinc must be taken from the diet because the body cannot produce it. It is mainly kept in bone and muscle. 14 g of zinc is required for adults in one day. Some vital benefits of consuming zinc are as follows:
- Boosts up the immune system
- Healing of the wound
- Less chance of blood clotting
- Treatment for the common cold
- Sharpens memory
- Promotes healthy thyroid function in people having hypothyroidism
- Increase the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Magnesium
You need magnesium for both your body and brain [13]. It has numerous advantages, including as:
- Lesser chance of thyroid disease
- Lower risk of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis disease
- Lowers blood pressure level
- The positive effect of thyroglobulin antibody (TGA)
- Improves premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Increases bone health
- Fights against inflammation
Iron
The body needs mineral iron for healthy development. Your body requires iron to create myoglobin proteins, which oxygenate muscles and hemoglobin and deliver oxygen from your lungs to all body areas. Iron is required by your body to create certain hormones. Iron intake in hypothyroidism leads to the following benefits:
- Less chance of thyroid disease
- Converts T4 hormone into T3
- Best for athletic performance
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Improves hair growth
- Regulates the temperature of the body
- Good for digestion
Vitamin D and vitamin B12
Autoimmune hypothyroidism is linked to low vitamin D levels. Therefore, healthcare measures could considerably reduce long-term hypothyroidism risk, including widespread vitamin D insufficiency screening among at-risk populations. A shortage in vitamin B12 affects over half of people with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis disease and hypothyroidism. In addition, the production of DNA, correct red blood cell development, and cognitive function depend on vitamin B12.
Which Foods are Best for Underactive thyroid?
Does your thyroid hormone function correctly? It is always important to eat what’s right. Eating foods that are good for thyroid patients helps maintain a good heart rate, metabolism, body temperature, and energy levels. While suffering from hypothyroidism, you must be aware of foods that are high in iodine, selenium, zinc, and magnesium because to eat is a necessity but to eat healthily is an art. You must have heard that balance is the key. So, to keep your iodine level balanced, you must consume the following foods.
Fruits and vegetable
Fruits highly rich in antioxidants are required to make your thyroid hormone function smoothly [14]. Blueberries, strawberries, and cranberries [15] contain good antioxidative property that helps in fighting against free radicals, which increases the risk of hypothyroidism, weight gain, hair loss, and fatigue.
Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, and keep your body healthy. Other fruits beneficial for hypothyroidism are apples, bananas, and avocados. Apples lower your cholesterol level, prevent diabetes, weight gain, and heart disease, and also helps strengthen your bones. On the other hand, avocado is a good source of iron, vitamin K, vitamin B6, vitamin C, and potassium.
Green leafy vegetables that treat hypothyroidism include kelp, green peppers, and sweet potatoes [16]. These vegetables are rich in antioxidants and help increase the absorption of the thyroid to produce thyroid hormones and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Spices and herbs
Ginger is a common spice consumed in hypothyroidism. It contains numerous health advantages of ginger, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial qualities. According to research performed in 2019 [17], it was concluded that a herb called Ashwagandha reduces oxidative stress and boosts thyroid hormones to improve thyroid function.
Black cumin is another vital herb that treats thyroid functions because it contains phytochemicals. It can generally enhance thyroid function for patients with hypothyroidism, according to a 2016 study investigating the impact of black cumin on Hashimoto’s thyroiditis condition [18].
Nuts and seeds
Zinc deficiency can also affect the functioning o the thyroid gland. Therefore, try to take this mineral up to the mark. Zinc is high in sunflower, sesame, pumpkin, and chia seeds. So to supply your body with zinc, add those seeds to your diet. People with hypothyroidism should eat Brazil nuts, hazelnuts, and macadamia nuts, which are considered a high source of selenium and help the thyroid function properly. One to two Brazil nuts per day meet the required daily allowance of iodine and selenium.

Avoid eating peanuts and walnuts as they interfere with the absorption of the thyroid, worsening hypothyroidism. Always focus on healthy eating. Almonds and cashews are also good sources in the treatment of hypothyroidism. They ensure the proper thyroid hormone functioning and protect thyroid tissues against oxidative stress, control cholesterol, maintain hormone profiles, and help people lose weight.
Legumes and beans
One of the best beans for hypothyroidism is chickpeas. Lentils, beans, and chickpeas should be eaten by people suffering from hypothyroidism because they are rich in zinc and selenium. Not only do beans and legumes reduce constipation, but they also help regulate the gastrointestinal tract, particularly bowel movements.
Whole grains
Whole grains eaten during hypothyroidism are quinoa, brown rice, sprouts, millets, whole wheat bread, amaranth, and oats which help in decreasing constipation and helping with bowel movements. In addition, since the body must work harder to digest whole grains, the added fiber speeds up metabolism.
Few people with hypothyroidism choose to avoid whole grains. Still, if you prefer to include them in your diet, you must eat them according to the recommended daily allowance.
Foods containing iodized table salt
Iodine must come from the foods containing the iodized table you eat since your body cannot produce it. Therefore, one spoonful of iodized salt must be added to your cooked food. Egg noodles, fortified cereals, and enriched pasta are mainly foods that contain iodized salt. For the most part, consuming a range of balanced food will be enough to fulfill your mineral demands in hypothyroidism.
Low-fat Yogurt
Low-fat yogurt, also known as Greek yogurt, is full of iodine and contains numerous advantages that support thyroid health and boost immunity. In addition, iodine and vitamin D are abundant in low-fat yogurt. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), 50% of iodine is present in low-fat yogurt, which is necessary for synthesizing thyroid hormones. Low-fat yogurt also prevents Hashimoto’s disease.
Saltwater fish
According to the American Thyroid Association, saltwater fish are another excellent source of iodine. Red snapper fish [19], wild salmon, tuna, and trout contain omega-3 fatty acids, iodine, and zinc that decrease the risk of goiters and improve the rate of metabolism of your body.
Seaweed
Iodine, a vital vitamin for normal thyroid function, is primarily found in seaweed. Seaweed contains antioxidants, flavonoids, and carotenoids that help your body prevent stomach pain, fight against diseases, lose weight, and reduce the risk of thyroid cancer. In addition, seaweed is highly nutritious in selenium, zinc, and iodine, increasing energy levels and improving mental development.
Whole eggs
Iodine, zinc, and selenium, minerals that help the thyroid, are highly rich in eggs, particularly the yolk. Your body needs 15% iodine and 20% selenium daily for the thyroid gland to operate appropriately, both found in one large egg. Moreover, it has been concluded that one large egg a day is essential for people suffering from hypothyroidism. Therefore, you should consume an egg daily to fulfill your body’s requirements.
Dairy Products
Iodine is rich in dairy products like low-fat yogurt, cheese, ice cream, and low-fat milk. You can also choose healthy fats and dairy products. The thyroid requires vitamin D and iodine to keep thyroid glands from enlarging and developing goiter. So to ensure you’re getting enough iodine, reward yourself with a low-fat serving of yogurt.

Dairy products improve levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in the condition of hypothyroidism. Eggs are also a good source of iodine, zinc, and selenium in dairy products.
What Foods Should You avoid?
Levothyroxine, a synthetic thyroid hormone, is frequently provided to people with hypothyroidism. However, according to some research, Levothyroxine may be less effectively absorbed when consumed alongside magnesium, carbohydrate, and iron-rich meals.
Moreover, several beverages and canned foods can reduce a drug’s effectiveness for anyone with a low level of iodine.
Gluten-rich foods
For people with autoimmune thyroid conditions, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, gluten-rich foods could be harmful. Therefore, you should go for a gluten-free diet. Foods high in gluten contain gut microbes that have dangerous effects on thyroid function, the cardiovascular system, and vitamin absorption. Foods that are rich in gluten [20]are:
- Wheat
- White bread
- Barley
- Rye
- Wheat crackers
- Triticale
- Flatbread
- Sourdough bread
- Bagels
- Whole wheat wraps
Use gluten-free diets for hypothyroidism
Goitrogens
Goitrogens are chemicals that interfere with the thyroid hormones. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is then released by the pituitary in response to this, encouraging the growth of thyroid tissue and ultimately resulting in goiter.
Goitrogens can lead to thyroid anomalies resulting in bad thyroid health. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and spinach are very low in goitrogens. It decreases the activation of goitrogenic activity for people suffering from hypothyroidism. Other foods that are rich in goitrogens are:
- Cabbage
- Soy
- Pearl millet
- Brussel sprouts
- Russian kale
- Raw cruciferous vegetables
- Broccoli
Ultra-processed foods
Ultra-processed foods [21] contain a high amount of sugar added to them. Reducing consumption of highly processed foods decreases the risk of hypothyroidism, control of weight (weight loss), and overall health.
Foods and drinks that are ultra-processed are:
- Hot dogs
- Canned foods
- Donuts
- Soda
- Junk foods
- Cake
- Cookies
The Bottom Line: Best diet for hypothyroid
If you have good health, you have everything. People with hypothyroidism should consume a diet with lots of fresh vegetables and fruits, iodine, protein-rich foods, and a low intake of whole-grain carbohydrates. You must be aware that the first wealth is health. First, however, a person must explore and find a diet that makes them feel healthy. This basic meal plan, however, might give you a general concept of what a healthy diet might involve for someone with hypothyroidism.
- Breakfast: a spinach omelet served with a berry smoothie and half avocado
- Lunch: chicken and chickpea salad with fresh vegetables and pumpkin seeds
- Dinner: stir-fried fish with lemon and black pepper served with lentil curry
FAQs
Are there specific foods that can help boost thyroid function in hypothyroidism?
While no specific foods can directly boost thyroid function, a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients can support overall thyroid health. This includes foods like lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
Should people with hypothyroidism avoid certain foods?
People with hypothyroidism may benefit from limiting or avoiding goitrogenic foods like cabbage, broccoli, soy, and millet. These foods can interfere with thyroid function when consumed in large amounts. Cooking or fermenting these foods can reduce their goitrogenic effects.
Are there any foods that are particularly beneficial for individuals with hypothyroidism?
Including selenium-rich foods like Brazil nuts, seafood, and eggs in the diet may be beneficial for thyroid health. Selenium is essential for the production and conversion of thyroid hormones.
Can a specific diet alone cure hypothyroidism?
While a healthy diet is important for overall well-being and supporting thyroid health, it cannot cure hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism is typically a chronic condition that requires medical treatment, such as thyroid hormone replacement therapy. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and management.
The Bottom Line
Many people worldwide suffer from hypothyroidism, sometimes known as an underactive thyroid. It can result in various symptoms, including tiredness, hair loss, bowel problems, anxiety, and weight gain. However, eating the right foods and using thyroid hormone replacement medication it may help you feel better, minimize your symptoms, and enhance your thyroid function.
Although everyone’s nutritional requirements differ, a diet high in whole, nutrient-dense foods, including leafy green vegetables, berries, nuts, and seafood, can benefit almost everyone with hypothyroidism.
References
1. Thyroid Problems: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment – PharmEasy [Internet]. PharmEasy Blog. 2018 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://pharmeasy.in/blog/thyroid-health-causes-symptoms-and-treatment/
2. Patil N, Rehman A, Jialal I. Hypothyroidism [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519536/
3. Cleveland Clinic. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid) Symptoms & More | Cleveland Clinic [Internet]. Cleveland Clinic. 2017 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12120-hypothyroidism
4. Cafasso J. Recognizing the Symptoms of Myxedema [Internet]. Healthline. Healthline Media; 2017 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/health/myxedema
5. Shahid MA, Sandeep Sharma. Physiology, Thyroid Hormone [Internet]. Nih.gov. StatPearls Publishing; 2019 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500006/
6.Taylor PN, Albrecht D, Scholz A, Gutierrez-Buey G, Lazarus JH, Dayan CM, et al. Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2018 Mar 23;14(5):301–16.
7. Vanderpump MPJ, Tunbrldge WMG, French JM, Appleton D, Bates D, Clark F, et al. The incidence of thyroid disorders in the community: a twenty-year follow-up of the Whickham Survey. Clinical Endocrinology. 1995 Jul;43(1):55–68.
8. González-Rodríguez LA, Felici-Giovanini ME, Haddock L. Thyroid dysfunction in an adult female population: A population-based study of Latin American Vertebral Osteoporosis Study (LAVOS) – Puerto Rico site. Puerto Rico health sciences journal. 2013;32(2):57–62.
9. Triggiani V, Tafaro E, Giagulli V, Sabba C, Resta F, Licchelli B, et al. Role of Iodine, Selenium and Other Micronutrients in Thyroid Function and Disorders. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders – Drug Targets. 2009 Sep 1;9(3):277–94.
10. Raman R. Best Hypothyroidism diet: Foods to Eat, Foods to Avoid [Internet]. Healthline. Healthline Media; 2019 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/hypothyroidism-diet#important-nutrients
11. 7 Science-Based Health Benefits of Selenium [Internet]. Healthline. 2017 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/selenium-benefits
12. Australia H. Zinc and your health [Internet]. www.healthdirect.gov.au. 2021 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/zinc#:~:text=Zinc%20is%20a%20mineral%20that
13. 12 Magnesium Health Benefits [Internet]. Healthline. 2022 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/magnesium-benefits
14. Jung SK, Kim K, Tae K, Kong G, Kim MK. The effect of raw vegetable and fruit intake on thyroid cancer risk among women: a case–control study in South Korea. British Journal of Nutrition. 2012 Mar 28;109(1):118–28.
15. Steer clear of thyroid problems by increasing consumption of these fruits [Internet]. Healthshots. 2021 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthshots.com/healthy-eating/superfoods/fruits-that-every-thyroid-patient-should-eat/
16. 7 Hypothyroidism-Friendly Foods to Add to Your Diet [Internet]. EverydayHealth.com. [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.everydayhealth.com/hs/thyroid-pictures/foods-to-eat/
18. Farhangi MA, Dehghan P, Tajmiri S, Abbasi MM. The effects of Nigella sativa on thyroid function, serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) – 1, Nesfatin-1 and anthropometric features in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Complementary and Alternative thyroid hormone replacement medication. 2016 Nov 16;16(1).
19. Herawati E, Titisari RS, Husna SAN, Astirin OP, Widiyani T, Listyawati S. Red snapper fish intake improves thyroid gland activity in the hypothyroidism rat. Food Research. 2021 Jun 20;5(S2):18–24.
20. 8 Foods to Avoid with a Gluten Intolerance (and 7 to Eat) [Internet]. Healthline. 2020 [cited 2022 Oct 4]. Available from: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/gluten-food-list
21. Zhang J, Zhu F, Cao Z, Rayamajhi S, Zhang Q, Liu L, et al. Ultra-processed food consumption and the risk of subclinical thyroid dysfunction: a prospective cohort study. Food & Function. 2022;13(6):3431–40.