Looking to boost your nutrient intake? There high chlorophyll sprouts to try! These 5 sprouts – alfalfa, broccoli, wheatgrass, sunflower, and mung bean – are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Add them to salads, wraps, soups, and smoothies for a nutritious boost to your diet.
Alfalfa sprouts
Alfalfa sprouts are one of the most popular types of sprouts, and for good reason. These small, crunchy sprouts are packed with nutrients and can be used in a variety of dishes, from sandwiches to salads and more. One of the key benefits of alfalfa sprouts is that they are a great source of vitamins and minerals. They contain vitamins A, C, E, and K, as well as calcium, iron, and magnesium. They are also high in antioxidants, which can help to protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Alfalfa sprouts are also known for their potential health benefits. They have been shown to help lower cholesterol levels, improve digestion, and support a healthy immune system. Additionally, they may have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.

One of the great things about alfalfa sprouts is that they are easy to grow at home. All you need is a jar or sprouting tray, some hot water only, and alfalfa seeds. Simply soak the sprouted seeds for a few hours, then rinse and drain them several times a day until they begin to sprout. Within a few days, you’ll have your own fresh, nutritious sprouts.
Alfalfa sprouts can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They can be added to salads, sandwiches, or wraps for a healthy crunch, or used as a topping for soups or stir-fries. They can also be blended into smoothies or juiced for a nutrient-packed drink.
It is important to note that alfalfa sprouts should be consumed fresh and raw to avoid the risk of foodborne illness. Because sprouts are grown in warm, moist conditions, they can be a breeding ground for bacteria if not handled properly. It is recommended to purchase sprouts from a reputable source, or to grow them yourself at home to ensure their safety.
Broccoli sprouts
Broccoli sprouts are one of the most nutrient-dense foods you can add to your diet. These tiny sprouts are packed with antioxidants and other health-promoting compounds that have been linked to a variety of potential health benefits. One of the key compounds found in broccoli sprouts is sulforaphane. This powerful antioxidant has been shown to have anti-cancer properties and may help to reduce the risk of several types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer. Sulforaphane may also help to protect against heart disease and other chronic illnesses by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body.
Broccoli sprouts are also a great source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate. They are also rich in fiber, which can help to promote healthy digestion and reduce the risk of certain digestive disorders, such as constipation and diverticulitis.

Another benefit of broccoli sprouts is that they are easy to grow at home. All you need is a jar or sprouting tray, some hot water, and broccoli seeds. Simply soak the sprouting seeds for a few hours, then rinse and drain them several times a day until they begin to sprout. Within a few days, you’ll have your own fresh, nutritious broccoli sprouts.
Broccoli sprouts can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They can be added to salads, sandwiches, or wraps for a healthy crunch, or used as a topping for soups or stir-fries. They can also be blended into smoothies or juiced for a nutrient-packed drink.
It is important to note that while broccoli sprouts are generally safe to consume, they can be a breeding ground for bacteria if not handled properly. It is recommended to purchase sprouts from a reputable source, or to grow them yourself at home to ensure their safety. Some people may experience some digestive tract discomfort when consuming large amounts of broccoli sprouts, so it is important to start with small amounts and gradually increase your intake over time.
Ways to Eat Broccoli Sprouts
Broccoli sprouts are a delicious and nutritious addition to any meal. They are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, and have been linked to numerous health benefits. Here are some ways to incorporate broccoli sprouts into your diet:
- Add them to sandwiches: Broccoli sprouts add a delicious crunch to sandwiches. Simply rinse the sprouts, pat them dry, and add them to your sandwich along with your favorite fillings.
- Toss them into salads: Broccoli sprouts make a great addition to any salad. Combine them with other greens, such as spinach or arugula, and top with your favorite veggies and a healthy dressing.
- Blend them into smoothies: Adding broccoli sprouts to your morning smoothie is a great way to start your day with a boost of nutrients. Blend them with your favorite fruits and veggies, such as bananas and spinach, for a delicious and nutritious drink.
- Use them as a garnish: Broccoli sprouts make a beautiful and nutritious garnish for any dish. Simply rinse them and place them on top of your dish for an added pop of color and flavor.
- Mix them into stir-fries: Add broccoli sprouts to your stir-fry for a boost of nutrition. They pair well with other veggies and protein sources, such as tofu or chicken.
- Top your pizza with them: Broccoli sprouts make a great topping for pizza. Simply sprinkle them on top of your favorite pizza before baking for an added crunch and boost of nutrition.
Incorporating broccoli sprouts into your diet is easy and delicious. Try out these ideas and experiment with different ways to enjoy these nutritious sprouts.
Getting the Most Sulforaphane from Broccoli Sprouts
Sulforaphane is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound found in high concentrations in broccoli sprouts. It has been linked to numerous health benefits, including cancer prevention, improved heart health, and better brain function. Here are some tips for getting the most sulforaphane from broccoli sprouts:
- Choose fresh sprouts: The fresher the broccoli sprouts, the higher the sulforaphane content. Look for sprouts that are crisp and green with no signs of wilting or yellowing.
- Use a blender: Research has shown that blending broccoli sprouts can increase sulforaphane production by up to 3 times compared to chewing them. Blend your sprouts with a small amount of water to create a smoothie or use them in a salad dressing.
- Add mustard seed powder: Mustard seed powder contains an enzyme that can help boost sulforaphane production. Adding a small amount of mustard seed powder to your broccoli sprouts can increase the amount of sulforaphane your body absorbs.
- Heat them up: Heating broccoli sprouts can also increase sulforaphane production. Lightly steam or sauté your sprouts before eating them to get the most out of their sulforaphane content.
- Pair them with a healthy fat: Sulforaphane is a fat-soluble compound, which means it is better absorbed when paired with a healthy fat source. Try adding some avocado or olive oil to your broccoli sprouts to help your body absorb more sulforaphane.
By following these tips, you can maximize the amount of sulforaphane you get from your broccoli sprouts and enjoy their many health benefits. Remember to always choose fresh sprouts and experiment with different preparation methods to find what works best for you.
What happens when you heat broccoli sprouts?
When you heat broccoli sprouts, the heat can break down the enzyme myrosinase that helps convert glucoraphanin, a precursor to sulforaphane, into active sulforaphane. This can potentially decrease the amount of sulforaphane your body can absorb from the broccoli sprouts.
However, research has shown that lightly steaming or sautéing broccoli sprouts can still lead to significant increases in sulforaphane production. In fact, one study found that lightly steaming broccoli sprouts for just 3-4 minutes increased sulforaphane production by up to 20-fold compared to raw sprouts. So while heating broccoli sprouts can potentially decrease their sulforaphane content, the cooking method and duration of growing sprouts can also have an impact on the amount of sulforaphane produced.
Wheatgrass sprouts
Wheatgrass sprouts are nutrient-dense, as they contain a range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They are rich in chlorophyll, which may help to detoxify the body, improve digestion, and boost immune function. In addition to chlorophyll, wheatgrass sprouts contain vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and several B vitamins. They are also a good source of iron, calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic acids are also found in wheatgrass sprouts.
These sprouts can be consumed raw or juiced, but their strong taste may require mixing with other fruits and vegetables to make it more palatable. Wheatgrass sprouts can also be used in smoothies or added to salads. It is important to note that wheatgrass sprouts are not suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, as they are derived from wheat. It is also recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating wheatgrass sprouts into the diet, as they may interact with certain medications or supplements.
Sunflower sprouts
Sunflower sprouts are young plants grown from the seeds of the sunflower plant. These sprouts are usually harvested within a week of germination, when the young plants have grown to about 2-3 inches tall. Sunflower sprouts are packed with nutrients and offer numerous health benefits.
One of the key benefits of sunflower sprouts is their high chlorophyll content. Chlorophyll is a pigment that gives plants their green color and is responsible for photosynthesis. It also has antioxidant properties and helps to detoxify the human body. Sunflower sprouts are a rich source of chlorophyll, which makes them an excellent addition to any diet.

In addition to their chlorophyll content, sunflower sprouts are also rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, B, C, and E, as well as calcium, iron, and zinc. They are also low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great choice for anyone looking to maintain a healthy weight.
Sunflower sprouts can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They can be added to salads, sandwiches, and smoothies, or used as a garnish for soups and stews. They have a mild, nutty flavor that complements a wide range of dishes. Plus, they are easy to grow at home, making them a convenient and cost-effective way to add more nutrients to your diet.
Red clover sprouts
Red- growing sprouts and seeds or clover sprouts and seeds are young plants or seeds grown from the seeds of the red clover plant. These sprouts or seeds are usually harvested within a week of germination, when the young plants or seeds have grown to about 2-3 inches tall. Red clover sprouts and seeds are known for their distinctive flavor and offer numerous health benefits. One of the key benefits of red clover sprouts is their high nutrient content. They are a rich source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and E, as well as calcium, iron, and magnesium. They also contain antioxidants that help to protect the body against free radical damage.
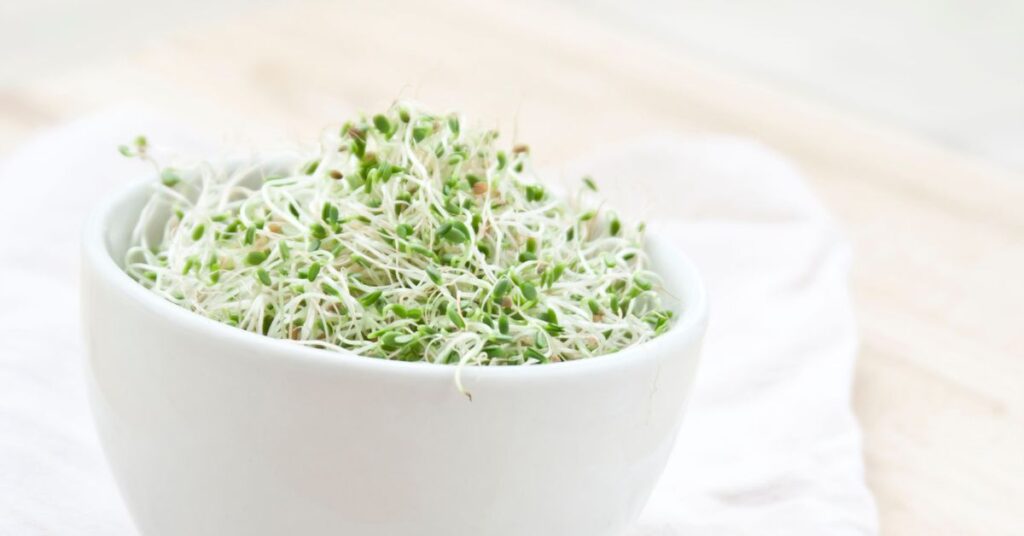

Red clover sprouts are also a good source of phytoestrogens, which are plant compounds that mimic the effects of estrogen in the human body. This makes them a popular choice for women experiencing symptoms of menopause. Red clover sprouts can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. They have a slightly sweet, nutty flavor that pairs well with a range of dishes. They can be added to salads, sandwiches, and wraps, or used as a garnish for soups and stews. They are also easy to grow at home, making them a convenient and cost-effective way to add more nutrients to your diet.
Kale sprouts
Kale sprouts are young shoots of kale plants that have just begun to grow from the kale seed. These sprouts are packed with nutrition and offer a range of health benefits. One of the main benefits of kale sprouts is their high content of antioxidants, which can help to protect the body against damage from free radicals. They are also a good source of vitamin C, vitamin K, and calcium.
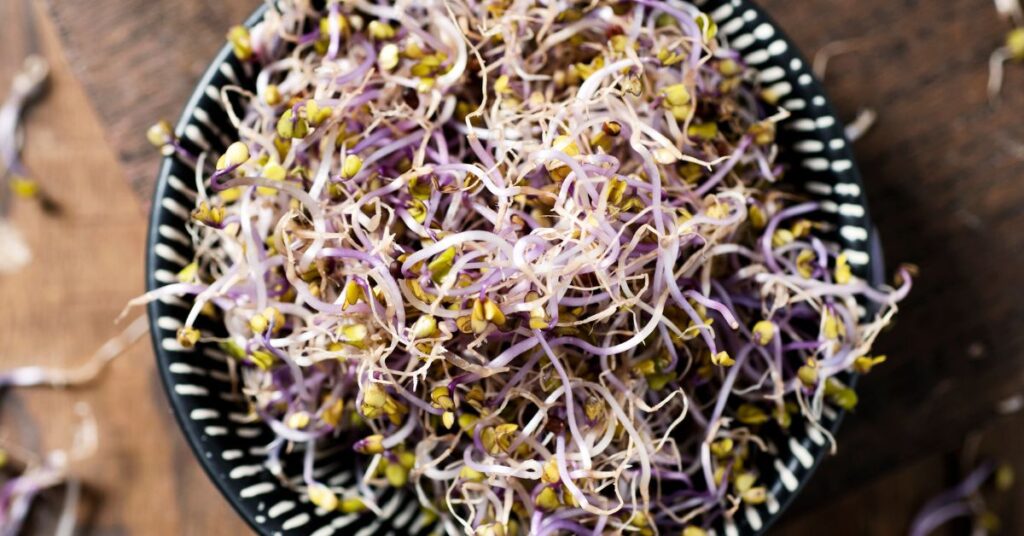

Kale sprouts have a mild, slightly nutty flavor and can be used in a variety of dishes. They are great in salads, sandwiches, and wraps, and can also be used as a topping for pizzas and soups. Kale sprouts can also be used in smoothies or juiced for a nutrient-packed beverage. Kale sprouts are easy to grow at home and can be harvested in as little as a week. They are a cost-effective way to add more nutrition to your diet and can be a fun and rewarding project for gardeners of all levels.
Pea sprouts
Pea sprouts, also known as pea shoots, are the young leaves and tendrils of the pea plant. They are often consumed as a salad green or added to sandwiches and wraps for added texture and flavor.
Pea sprouts are a rich source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate and fiber. They also contain antioxidants such as flavonoids and carotenoids, which have been linked to a range of potential health benefits including reducing inflammation and protecting against chronic diseases.
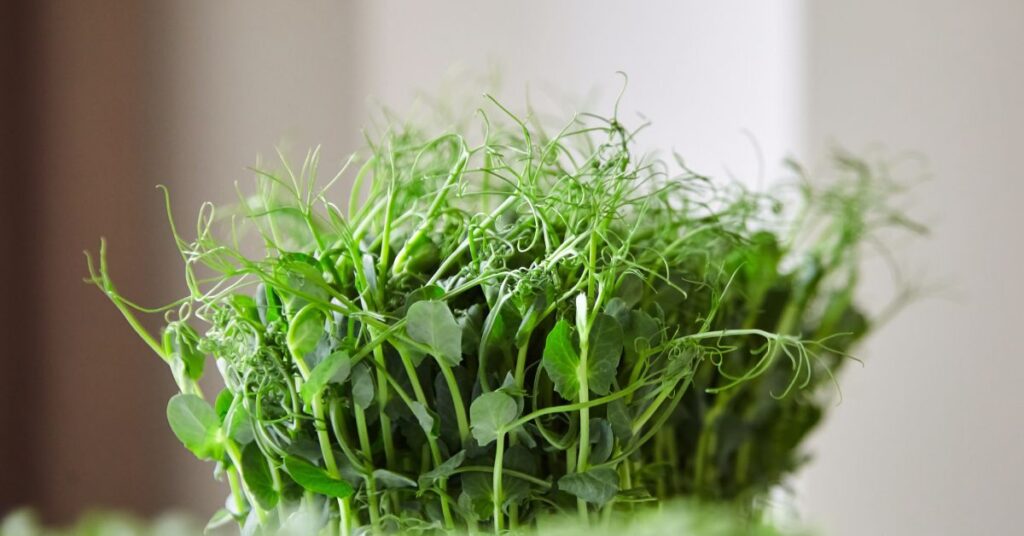

In addition to their nutritional value, pea sprouts are easy to grow at home and can be harvested in just a few weeks. They can be grown in soil or in a hydroponic system, making them a convenient option for individuals with limited outdoor space.
Pea sprouts can be consumed raw or lightly cooked, and their delicate flavor pairs well with a variety of dishes. They can be added to soups and stews, used as a topping for pizzas and flatbreads, or blended into pesto or hummus for added nutrition.
Mung bean sprouts
Mung bean sprouts are one of the most commonly consumed sprouts around the world. They are made by the germinating seeds from mung beans until they form small sprouts. These sprouts are a popular ingredient in many Asian dishes, including stir-fries, salads, and soups.
Mung bean sprouts are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a healthy addition to any diet. They are a good source of protein, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, iron, and potassium. Mung bean sprouts also contain antioxidants that can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation.
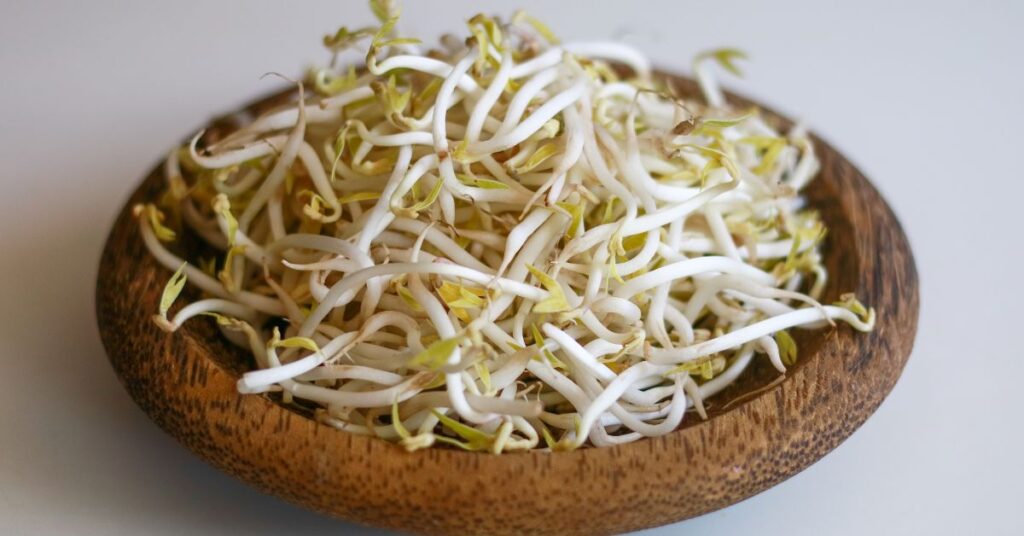

Mung bean sprouts are easy to grow at home, and can be used in a variety of dishes. They can be consumed raw or lightly cooked, and their mild flavor makes them a versatile ingredient in many recipes. Mung bean sprouts can be added to stir-fries, salads, sandwiches, and wraps, or used as a topping for soups and noodle dishes. They can also be blended into smoothies or juiced for added nutrition.
Brussel sprouts
Brussel sprouts, also known as mini cabbages, are a type of cruciferous vegetable that belong to the same family growing plants as broccoli, kale, and cauliflower. They are a low-calorie and nutrient-dense food that are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
One of the key nutrients found in Brussels sprouts is vitamin C, which plays an important role in immune function and collagen production. They are also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for blood clotting and bone health, as well as vitamin A, which supports healthy vision and skin.
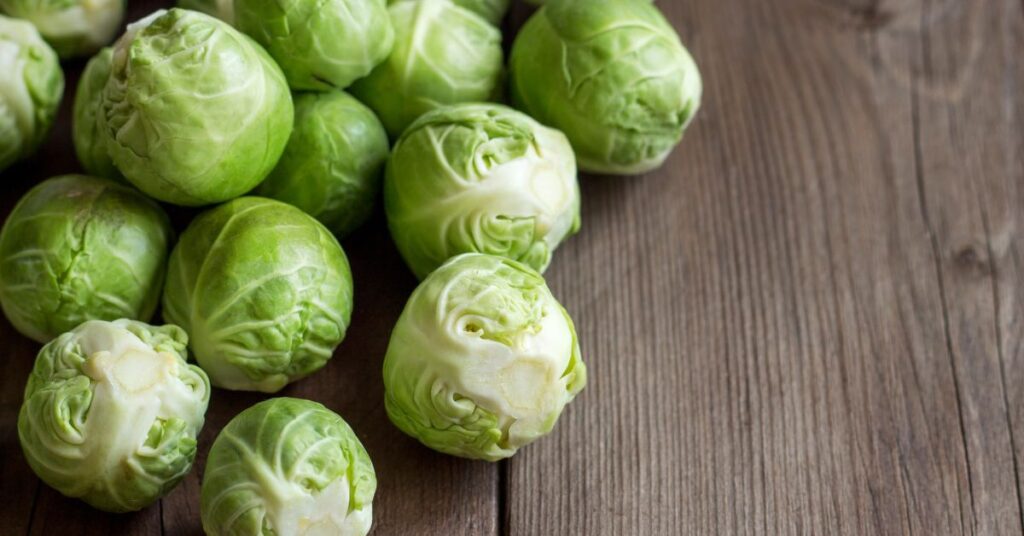

In addition to vitamins, Brussels sprouts are also rich in minerals like potassium, which helps regulate blood pressure, and folate, which is essential for DNA synthesis and cell division. They also contain antioxidants like quercetin and kaempferol, which have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties.
Brussels sprouts are a versatile ingredient that can be roasted, sautéed, or steamed and added to a wide range of dishes, from salads and stir-fries to pasta dishes and casseroles. They are a great addition to a healthy and balanced diet and can provide a variety of health benefits.
Are brussel sprouts high in chlorophyll?
Yes, Brussels sprouts green peas are high in chlorophyll. This nutrient gives the vegetable its green color and is responsible for many of the health benefits associated with Brussels sprouts.
Chlorophyll is a type of pigment that is found in plants and is responsible for different plants their green color. It is important green plants because it plays a role in the process of photosynthesis, which is how plants produce energy from sunlight.
In addition to its role in photosynthesis, chlorophyll is also associated with a variety of health benefits. It is a powerful antioxidant, which means it can help to protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. It has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
Brussels sprouts are also a good source of other important nutrients, including vitamin C, vitamin K, and fiber. They are low in calories and high in antioxidants, making them a great addition to any healthy diet.
To maximize the amount of chlorophyll you get from Brussels sprouts, it is best to eat them raw or lightly cooked. This will help to preserve the nutrients in the vegetable and ensure that you get the most health benefits possible.
Mustard Seed Sprouts
Mustard seed sprouts are young plants that are grown from the seeds of the mustard plant. They are a popular sprout variety due to their strong, spicy flavor and many potential health benefits. Mustard seed sprouts are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a great addition to a healthy and balanced diet.
One of the key nutrients found in mustard seed sprouts hard seeds is vitamin C, which supports immune function and collagen production. They are also a good source of vitamin K, which is important for blood clotting and bone health. Mustard seed suppliers, seeds moist other seed sprouts contain minerals like calcium and iron, which are essential for strong bones and healthy, red blood cells.
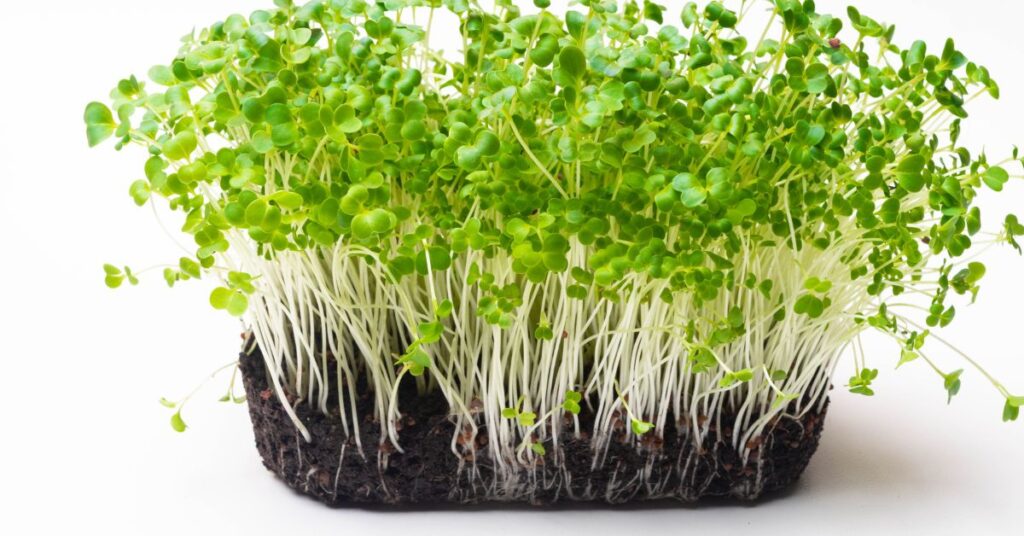

Mustard seed sprouts are also rich in antioxidants like phenols and flavonoids, which can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation. Studies have shown that these antioxidants may have anti-cancer properties.
Mustard seed sprouts have a strong, spicy flavor that pairs well with many dishes. They can be added to sandwiches, salads, wraps, and stir-fries to add flavor and texture. Overall, mustard seed sprouts are a nutrient-dense food that can provide a range of potential health benefits.
Buckwheat Sprouts
Buckwheat sprouts are young plants that are grown from the seeds of the buckwheat plant. They are a popular sprout variety due to their nutty flavor and many potential health benefits. Buckwheat sprouts are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them a great addition to a healthy and balanced diet.
One of the key nutrients found in buckwheat sprouts is fiber, which supports healthy digestion and can help lower cholesterol levels. They are also a good source of B vitamins like niacin, thiamin, and riboflavin, which are essential for energy production and overall good health too.
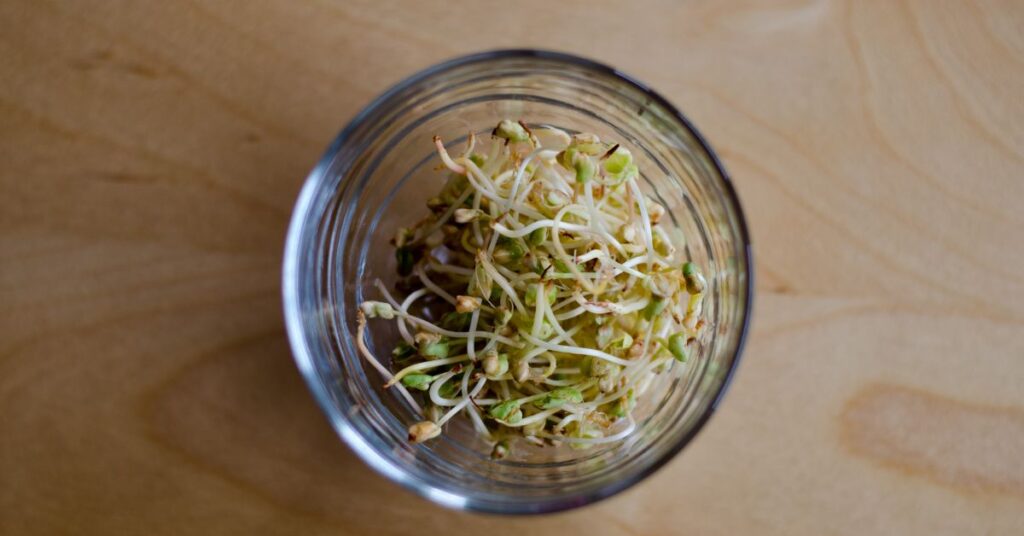

Buckwheat sprouts are also rich in minerals like magnesium, which is important for bone and cardiovascular health too, and manganese, which supports healthy brain function. They are also a good source of antioxidants like rutin, which can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation.
Buckwheat sprouts can be added to a variety of dishes, from salads and sandwiches to soups and stir-fries. They can also be used to make sprouted buckwheat flour, which is a nutritious and gluten-free alternative to regular flour. Overall, buckwheat sprouts are a nutrient-dense food that can provide a range of potential health benefits.
Which sprouts are more healthy?
All sprouts are healthy and provide a range of potential health benefits. However, some sprouts may be more nutrient-dense than others, depending on their specific nutritional profile. Broccoli sprouts, for example, are one of the most nutrient-dense sprout varieties, as they are rich in sulforaphane, a compound that has been linked to potential anti-cancer properties. Alfalfa sprouts are also a popular sprout variety due to their high vitamin C and antioxidant content.
Other sprouts that are commonly considered to be healthy include mung bean sprouts, which are a good source of protein, fiber, and B vitamins, and wheatgrass sprouts, which are rich in chlorophyll and may help support healthy blood flow.
Ultimately, the best sprouts for you will depend on your individual nutritional needs overall health, and preferences living food itself. Adding a variety of sprouts to your diet can help ensure that you are getting a wide range of nutrients and potential health benefits. It is important to note, however, that sprouts should be consumed raw or lightly cooked, as cooking can destroy some of their beneficial compounds. Additionally, it is important to properly store and handle sprouts to avoid the risk of foodborne illness.
Timing: Eat or Freeze the Sprouts Right Away
Timing is an important consideration when it comes to eating or storing sprouts. While sprouts are a nutritious and delicious addition to many meals, they are also perishable and can quickly spoil if not handled properly. One option for preserving the freshness of sprouts is to eat them right away. Freshly sprouted seeds or legumes can be enjoyed in salads, sandwiches, wraps, or smoothies. Sprouts can also be used in stir-fries, soups, or other cooked dishes.
However, if you can’t eat your sprouts right away, it’s important to store them properly. If left at room temperature, sprouts can quickly spoil and become unsafe to eat. The best way to store sprouts is to keep them in a sealed container in the refrigerator. This will help keep them fresh for a few days.
If you have a large quantity of sprouts, you can also consider freezing them for later use. To freeze sprouts, first blanch them in boiling water for a few seconds and then plunge them into ice water. Pat them dry and then place them in an airtight container in the freezer. Frozen sprouts can last for up to six months. It’s important to eat or freeze sprouts right away to ensure their freshness and safety. Whether you choose to eat them raw or cooked, sprouts can be a nutritious and delicious addition to your diet.
Are sprouts high in chlorophyll?
Yes, sprouts turn green from dry seeds eating fresh sprouts purchase seeds are generally high in chlorophyll, a green pigment found in plants. Chlorophyll is responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Sprouts are often grown from seeds or legumes that are rich in chlorophyll, such as alfalfa, wheatgrass, and broccoli. During the sprouting process, the seed or legume undergoes rapid growth and develops a high concentration of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll has been linked to potential health benefits, including improved digestion, increased energy, and potential anti-inflammatory properties.
Additionally, chlorophyll is a rich source of antioxidants, which can help protect the body from free radical damage. It’s worth noting that not all sprouts are created equal when it comes to their chlorophyll content. Some sprout varieties, such as wheatgrass and barley grass, are particularly high in chlorophyll, while others may have lower concentrations.
The amount of chlorophyll in sprouts can also vary depending on the growing conditions and harvesting methods. Sprouts are generally high in chlorophyll, which can provide a range of potential health benefits. Incorporating a variety of sprouts into your diet can help ensure that you are getting a wide range of nutrients, including chlorophyll.
Which sprout has the highest nutrient?
While all sprouts are nutrient-dense, some sprouts are particularly high in specific vitamins, minerals soluble fiber, and antioxidants. Here are a few examples of sprouts that are especially nutrient-rich:
- Broccoli Sprouts: Broccoli sprouts are a potent source of sulforaphane, a compound that has been linked to potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation and potentially lowering the risk of certain types of cancer. They are also high in vitamins C and K, and contain a range of antioxidants.
- Alfalfa Sprouts: Alfalfa sprouts are a good source of vitamin K, which is important for blood clotting and bone health. They also contain a range of other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, folate, and iron.
- Radish Sprouts: Radish sprouts are high in vitamin C and folate, and are also a good source of glucosinolates, which are compounds that have been linked to potential anti-cancer properties.
- Sunflower Sprouts: Sunflower sprouts are rich in vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect the body from free radical damage. They also contain a range of other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B6, iron, and zinc.
- Pea Shoots: Pea shoots are a good source of vitamin C, vitamin A, and folate. They also contain a range of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
It’s worth noting that the nutrient content of sprouts can vary depending on the growing conditions and harvesting methods. However, incorporating a variety of sprouts into your diet can help ensure that you are getting a wide range of nutrients.
L-ascorbic Acid Content in Sprouts and Microgreens!
L-ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the body’s immune system, wound healing, and the production of collagen. Many sprouts and microgreens are rich sources of vitamin C, making them a great addition to a healthy diet.
The amount of vitamin C in sprouts and microgreens can vary depending on the specific plant variety, growing conditions, and harvesting methods. However, several studies have shown that many sprouts and microgreens contain high levels of vitamin C.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Food Science found that broccoli sprouts contained high levels of vitamin C, with an average content of 72.8 mg per 100 grams of fresh weight. Similarly, another study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that pea microgreens had a vitamin C content of 59.3 mg per 100 grams of fresh weight.
Other sprouts and microgreens that are particularly high in vitamin C include red cabbage, kale, mustard, and arugula. Incorporating these sprouts and microgreens into your diet can help boost your vitamin C intake, which may have a range of potential health benefits. It’s important to note that vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, which means that it can be easily destroyed by heat and light. To preserve the vitamin C content of sprouts and microgreens, it’s best to consume them raw or lightly cooked.
Polyphenol Content in Sprouts and Microgreens!
Polyphenols are a type of plant compound that have been linked to a range of potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and potentially lowering the risk of certain types of cancer. Many sprouts and microgreens are rich sources of polyphenols, making them a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
The polyphenol content of sprouts and microgreens can vary depending on the specific plant variety, growing conditions, and harvesting methods. However, several studies have shown that many sprouts and microgreens contain high levels of polyphenols.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that red cabbage microgreens contained high levels of polyphenols, with an average content of 320.9 mg per 100 grams of fresh weight. Similarly, another study published in the Journal of Functional Foods found that broccoli sprouts contained high levels of polyphenols, with an average content of 233.8 mg per 100 grams of fresh weight. Other sprouts and microgreens that are particularly high in polyphenols include kale, arugula, and radish. Incorporating these sprouts and microgreens into your diet can help boost your polyphenol intake, which may have a range of potential health benefits.
It’s worth noting that polyphenols are also sensitive to heat and light, so to preserve their content, it’s best to consume sprouts and microgreens raw or lightly cooked. Additionally, since polyphenol content can vary depending on the growing conditions and harvesting methods, it’s a good idea to choose fresh, high-quality sprouts and microgreens from a reputable source.
Basic Chemical Composition of Sprouts and Microgreens:
Sprouts and microgreens are young plants that are harvested just after germination. They are nutrient-dense foods that are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Here is a breakdown of the basic chemical composition of sprouts and microgreens:
- Carbohydrates: Sprouts baby greens and microgreens are low in carbohydrates and are often used as a low-carb alternative to grains like rice or pasta. They contain simple carbohydrates like glucose and fructose, as well simple sugars such as complex carbohydrates simple sugars like starch.
- Protein: Sprouts and microgreens are an excellent source of plant-based protein. The protein content varies depending on the type of sprout or microgreen, but most contain between 10-25% protein by weight. The protein in sprouts and microgreens is easily digestible and contains all the essential amino acids.
- Fiber: Sprouts and microgreens are a good source of dietary fiber, which is important for digestive and cardiovascular health too. They contain both a soluble fiber and insoluble fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels, lower cholesterol, and promote feelings of fullness.
- Vitamins: Sprouts and microgreens are packed with vitamins, including vitamins A, C, E, and K, as well as B vitamins like folate and riboflavin. Vitamins are essential for maintaining healthy skin, eyes, and immune function, and for producing energy.
- Minerals: Sprouts and microgreens are a rich source of minerals like calcium, iron, magnesium, and potassium. These minerals are important for building strong bones and teeth, maintaining healthy blood pressure and heart function, and for energy production.
- Phytonutrients: Sprouts and microgreens contain a variety of phytonutrients, including carotenoids, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds. These plant-based compounds have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease.
Top Ranking Chlorophyll Content Food Items
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in plants that plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. In addition to its role in plant growth, chlorophyll has also been linked to a range of potential health benefits in humans, including reducing inflammation, promoting healthy digestion, and potentially even fighting cancer. Many foods contain chlorophyll, but some raw foods are particularly high in this green pigment. Here are some of the top ranking chlorophyll content food items:
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are some of the most chlorophyll-rich foods available. This includes spinach, kale, collard greens, and Swiss chard. For example, one cup of chopped raw spinach contains approximately 23.7 mg of chlorophyll.
Herbs
Many herbs are also rich in chlorophyll, including parsley, basil, cilantro, and dill. For example, one tablespoon of chopped parsley contains approximately 0.1 mg of chlorophyll.
Algae
Algae are a type of aquatic plant that are particularly high in chlorophyll. This includes spirulina and chlorella, two types of blue-green algae that are often used in supplements. For example, one tablespoon of spirulina powder contains approximately 29 mg of chlorophyll.
Wheatgrass
Wheatgrass is a type of young, wheat grass or plant that is often consumed as a juice or powder. It is particularly high in chlorophyll, with some sources suggesting that it contains up to 70% chlorophyll by weight.
Broccoli Sprouts
Broccoli sprouts are young broccoli plants that are grown specifically for their sprouts. They are known to be particularly high in sulforaphane, a compound that has been linked to potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation and fighting cancer. They are also high in chlorophyll, with one study suggesting that they contain up to 10 times as much chlorophyll as mature broccoli.
Spinach Powder
Spinach powder is made by grinding up dehydrated spinach leaves. It is often used as a supplement or ingredient in smoothies and other recipes. It is particularly high in chlorophyll, with one tablespoon of spinach powder containing approximately 42.2 mg of chlorophyll.
Brussels Sprouts
Brussels sprouts are a type of cruciferous vegetable that are often consumed roasted or steamed. They are known to be high in fiber and vitamin C, but they are also a good source of chlorophyll. For example, one cup of raw Brussels sprouts contains approximately 18.5 mg of chlorophyll.
Green Peppers
Green peppers are a type of bell pepper that are harvested before they have ripened to their full color. They are often used in salads and stir-fries, and they are also a good source of chlorophyll. For example, one cup of chopped green pepper contains approximately 6.9 mg of chlorophyll.
Green Beans
Green beans are a type of legume that are often eaten steamed or sautéed. They are a good source of fiber and vitamin C, and they are also a good source of chlorophyll. For example, one cup of raw green beans contains approximately 4.6 mg of chlorophyll.
Arugula
Arugula is a leafy green vegetable that is often used in salads and sandwiches. It is known for its slightly bitter taste and peppery flavor. It is also a good source of chlorophyll, with one cup of raw arugula containing approximately 15.6 mg of chlorophyll.
Spinach
Spinach is another leafy green vegetable that is packed with chlorophyll. This nutrient gives spinach its vibrant green color, and it is also responsible for so many seeds of the health benefits associated with this vegetable. Like kale, spinach is also high in vitamins A and C, as well as iron and other important minerals. It is also a good source of antioxidants, which can help to protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. One of the great things about spinach is that it is incredibly versatile. You can eat it raw in a salad, sauté it with other vegetables, or add it to smoothies for a nutrient-packed drink.
Parsley
Parsley is an herb that is commonly used in cooking, but it is also a nutritional powerhouse. It is rich in chlorophyll, vitamins A and C, and other important nutrients. In addition to its nutritional benefits, parsley is also known for its ability to freshen breath and promote healthy digestion. It is often used as a natural remedy for bad breath and other digestive issues. You can add parsley to soups, salads, and other dishes for a burst of flavor and nutrition. You can also use it to make pesto, which is a delicious and healthy sauce that can be used in a variety of ways.
Do sprouts contain amino acids?
Yes, sprouts contain amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. Amino acids are essential for various functions in the body, including muscle building, hormone synthesis, and immune function. Sprouts are particularly high in essential amino acids, which the body cannot produce on its own and must obtain from dietary sources. Some of the amino acids found in sprouts include lysine, leucine, and valine, which are important for maintaining and repairing tissues in the body.
Healthy Breakfast Ideas: How to Consume SPROUTS | Health Benefits of Consuming Sprouts | Weight Loss
FAQs
Can I grow high chlorophyll sprouts at home?
Yes, you can easily grow high chlorophyll sprouts at home. All you need is a sprouting jar, some seeds, and water. You can find sprouting jars and seeds at your local health food store or online.
How do I store high chlorophyll sprouts?
High chlorophyll sprouts should be stored in the refrigerator in a container with a lid. They will last for several days in the refrigerator.
Are high chlorophyll sprouts safe to eat?
Yes, high chlorophyll sprouts are safe to eat as long as they are grown and stored properly. It is important to rinse all the sprouts off thoroughly before eating them to remove any bacteria.
Can high chlorophyll sprouts help me lose weight?
High chlorophyll sprouts are low in calories and high in fiber, which can help with weight loss. They can also help you feel full and satisfied, which may prevent overeating.
How do I incorporate high chlorophyll sprouts into my diet?
High chlorophyll sprouts can be added to a variety of dishes, including sandwiches, salads, wraps, soups, and stir-fries. You can also blend them into smoothies or juice them for a healthy drink.
Are high chlorophyll sprouts more nutritious than other types of sprouts?
While all sprouts are nutritious, high chlorophyll sprouts are particularly beneficial due to their high levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They are also low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great addition to any healthy diet.
Conclusion
High chlorophyll sprouts are a delicious and nutritious addition to any diet. They are easy to grow at home and can be added to a variety of dishes for a boost of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
By trying out the 6 types of high chlorophyll sprouts mentioned in this blog post, you can add some variety to your sprouting routine and reap the many good health benefits that these sprouts provide. So go ahead and try them out – your body will thank you!