Yes, freeze-drying can remove chlorophyll from plants, but the extent of the loss depends on various factors.
What is Freeze-Drying?
Freeze-drying is a preservation process that removes water from perishable materials while they are in a frozen state. This technique of freeze dryers and vacuum drying is commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical industries to extend shelf life and preserve delicate materials that would otherwise deteriorate quickly.
Does Freeze Drying Remove Chlorophyll?
Yes, freeze-drying can remove chlorophyll from plant materials. Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in plants that plays a key role in photosynthesis. During the freeze-drying process, plant materials are exposed to low temperatures hot air drying and a vacuum, which can cause the chlorophyll to break down and be lost.
However, the extent to which freeze-drying removes chlorophyll depends on the specific plant material being used respectively the final color processed and the conditions of the freeze-drying process. In some cases, chlorophyll may be partially or fully retained, while in others it may be largely removed.

Overall, while freeze-drying is an effective method of drying the cannabis plant and preserving plant materials, its impact on the chlorophyll content of the material should be taken into account when considering its suitability for specific applications.
Why is Chlorophyll Important?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in plants that is essential for the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy in the form of glucose. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
In addition to its critical role in photosynthesis, chlorophyll has been found to have a range of health benefits for humans, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It has also been shown to promote healthy digestion, boost immune function, and even help prevent certain types of cancer. Overall, chlorophyll is a vital component of both plant and human health.
Other Ways to Preserve Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a delicate pigment that is susceptible to degradation and loss during preservation processes. While freeze-drying may result in the loss of chlorophyll, there are other ways to preserve this important compound.
One option is to use low-temperature, drying and curing methods, such as air-drying or oven-drying. These methods can help to preserve chlorophyll by minimizing exposure to heat and oxygen, which can cause degradation. However, it is important to note that even with these methods, some loss of chlorophyll may occur.
Another option is to use chemical preservatives, such as sodium metabisulfite or citric acid. These compounds can help to stabilize chlorophyll and prevent its degradation during storage. However, it is important to use these preservatives in moderation, as they can have negative effects on the flavor and texture of the preserved material.
Ultimately, the best method for preserving chlorophyll will depend on the specific material being preserved and the desired outcome. In some cases, a combination of preservation heat treatment methods may be necessary to achieve optimal results.
Sources of chlorophyll in food
Chlorophyll is found in many plant-based foods, including green leafy vegetables, herbs, and algae. It is responsible for their green color and has been linked to numerous health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Incorporating chlorophyll-rich foods into your diet can help promote overall health and wellbeing.
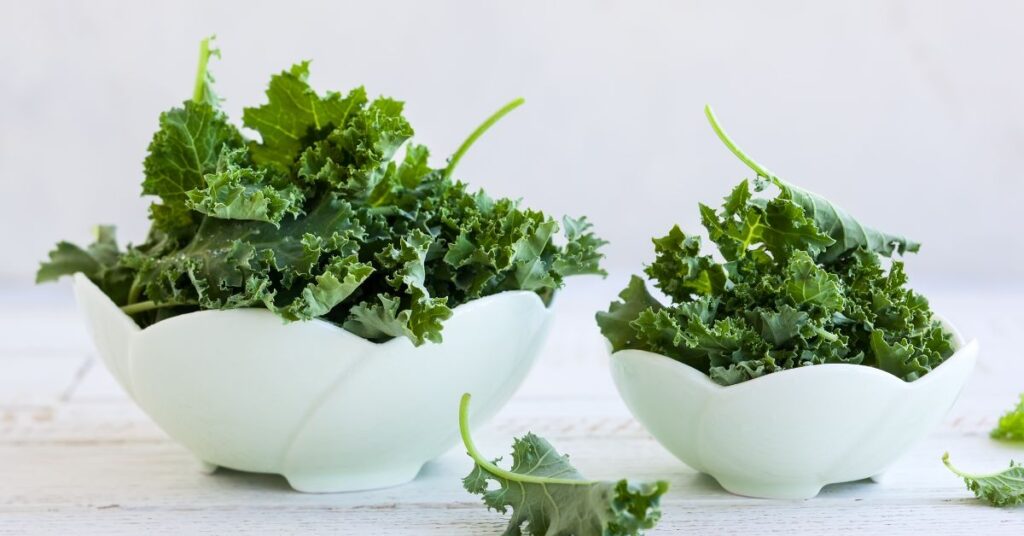

Some common sources of chlorophyll in food include green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale, and collard greens, as well as herbs such as parsley, cilantro, and basil. Other sources include algae such as chlorella and spirulina, and certain fruits and vegetables such as broccoli, green beans, and peas.
Nutritional value of chlorophyll
While chlorophyll itself is not a nutrient, it is found in many nutrient-rich foods. Chlorophyll-rich foods are high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals such as iron, magnesium, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases.
Benefits of consuming chlorophyll
Consuming chlorophyll rich foods has been associated with a range of health benefits, including improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and enhanced detoxification. Additionally, some studies have suggested that chlorophyll may have anti-cancer properties, although more research is needed to fully understand its potential health benefits.
Impact of Freeze Drying on Chlorophyll:
Freeze-drying can cause the breakdown and loss of chlorophyll in plant materials due to exposure to low temperatures and vacuum conditions. However, the extent of chlorophyll loss depends on the specific material being processed and the conditions of the freeze-drying process.
Effect of temperature on chlorophyll
High temperatures can cause the breakdown and loss of chlorophyll in plant materials, which can lead to discoloration and degradation of quality. However, low temperatures can also have a negative impact on chlorophyll in plant tissues, such as in the case of freeze-drying, which can result in its breakdown and loss.
Chemical changes that occur during freeze drying
During freeze-drying, water in the material being processed is removed through sublimation, which can cause chemical changes such as the denaturation of proteins and degradation of some compounds. These changes can affect the quality and functionality of the final product.
Research studies on chlorophyll content in freeze-dried food
Several research studies have investigated the impact of freeze-drying on the chlorophyll content of various food materials, including fruits, vegetables, and herbs. The results of these studies have shown that freeze-drying can cause significant losses of chlorophyll in some cases, while in others the losses may be minimal.
Advantages of Freeze Drying for Chlorophyll Preservation
Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilization, is a preservation method that involves removing water from a material through sublimation, resulting in a dried product that can be stored for extended periods of time. While freeze-drying can cause the breakdown and loss of chlorophyll in some cases, it also offers several advantages for chlorophyll preservation compared to other preservation methods.
- Preservation of Nutrient Content: One of the main advantages of freeze-drying for chlorophyll preservation is that it can help to preserve the nutrient content of the material being processed. Unlike other preservation methods such as high-temperature drying, freeze-drying involves minimal heat exposure, which can help to retain the nutritional value of the material. In fact, some studies have suggested that freeze-drying may help to preserve more of the vitamins and antioxidants in plant materials compared to other drying methods.
- Retention of Green Color: Another advantage of freeze-drying for chlorophyll preservation is that it can help to retain the green color of plant materials. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of plants, and can be degraded or lost during processing if the conditions are not optimal. However, freeze-drying can help to preserve the green color of plant materials by minimizing the exposure to high temperatures and oxygen that can cause degradation.
- Effect on Taste and Texture: Freeze-drying can also help to preserve the taste and texture of plant materials, which can be important for maintaining their sensory properties. While other preservation methods such as canning or high-temperature drying can result in changes to the taste and texture of plant materials, freeze-drying involves minimal heat exposure and can help to retain the natural flavors and textures of the material.
However, it should be noted that freeze-drying can also have some drawbacks for chlorophyll preservation. For example, the low temperatures and vacuum conditions used in freeze-drying can cause the breakdown and loss of chlorophyll in some cases. Additionally, the effectiveness of freeze-drying for chlorophyll preservation may depend on the specific material being processed, as well as the conditions of the freeze-drying process.
Factors Affecting Chlorophyll Retention in Freeze Drying
Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilization, is a popular preservation method used to remove water from materials while retaining their structure and properties. Chlorophyll is one of the key components of many plant-based materials, and its preservation during freeze-drying is an important consideration for maintaining the quality and nutritional value of these materials. Several factors can affect chlorophyll retention during freeze-drying, including the following:
Temperature
The temperature used during the freeze-drying and curing process can have a significant impact on chlorophyll retention. Lower temperatures are generally preferred for preserving chlorophyll, as higher temperatures can cause chlorophyll degradation and loss. However, excessively low temperatures can also lead to ice crystal formation, which can damage the structure of all the cell walls and material being processed and reduce chlorophyll retention.

Pressure
The vacuum pressure conditions used during freeze-drying can also affect chlorophyll retention. Vacuum conditions are typically used to remove moisture during the freeze-drying process, and the pressure conditions low temperature vacuum dehydration can impact the preservation of chlorophyll. In general, lower pressures are preferred for preserving chlorophyll, as higher pressures can lead to chlorophyll degradation and loss.
Oxygen Exposure
Exposure to oxygen during freeze-drying can also impact chlorophyll retention. Oxygen can cause the breakdown of chlorophyll and other compounds in plant-based materials, leading to degradation and loss. To minimize oxygen exposure, some freeze-drying processes are carried out under inert gas atmospheres, such as nitrogen.
Material Properties
The properties of the material being processed can also impact chlorophyll retention during freeze-drying. Factors such as the thickness and structure of the material, as well as its moisture content, can all influence the effectiveness of the freeze-drying process for preserving chlorophyll. In general, thinner materials with lower moisture contents are easier to freeze dry process, and can result in higher chlorophyll retention.
Pre-treatment
Pre-treatment of the material being processed can also impact chlorophyll retention during freeze-drying. For example, blanching the material prior to freeze-drying can help to preserve chlorophyll by inactivating enzymes that can cause degradation. Other pre-treatment methods, such as adding antioxidants, may also help to preserve chlorophyll during freeze-drying.
Storage Conditions
The storage conditions of the freeze-dried material can also impact chlorophyll retention over time. Factors such as storage temperature used, humidity, and exposure to light can all affect the stability of chlorophyll and other components in the material. To maximize chlorophyll retention, freeze-dried materials should be stored under appropriate conditions to minimize degradation.
Several factors can impact chlorophyll retention during freeze-drying, including temperature, pressure, oxygen exposure, material properties other drying method, pre-treatment, and storage conditions. By optimizing these factors, it is possible to maximize chlorophyll retention and preserve the quality and nutritional value of plant-based materials.
Challenges in Freeze Drying Chlorophyll-containing Foods
Freeze drying is an effective method of preserving chlorophyll-containing foods, but it is not without its challenges. The process of freeze dried samples involves removing water from the food through sublimation, which can cause changes in the structure and composition of the food. These changes can affect the retention of chlorophyll and other nutrients, as well as the taste and texture of the food.
One challenge in freeze drying chlorophyll-containing foods is the potential for oxidation. Chlorophyll is sensitive to oxygen and can degrade rapidly when exposed to it. To prevent oxidation, the food must be properly packaged and stored in an oxygen-free environment.
Another challenge is the potential for heat damage. Freeze drying involves heating the food to sublimate the water, which can cause heat damage to the chlorophyll and other heat-sensitive nutrients. To minimize heat damage, the temperature and duration of the freeze drying process must be carefully controlled.

The freeze drying process can also cause changes in the texture of the food. As the water is removed, the freeze dry food can become more brittle and lose its original texture. To prevent this, the food may need to be treated with cryoprotectants before freeze drying, which can help maintain its structure and texture.
Finally, using freeze dried cannabis for drying can be a costly and time-consuming extraction process itself. It requires specialized equipment and skilled operators, which can drive up the cost of production. Additionally, the process of freeze drying cannabis can take several hours or even days to complete, depending on the type of food and the desired level of dehydration.
While freeze drying is an effective method of preserving chlorophyll-containing foods, it is not without its challenges. The potential for oxidation, heat damage, changes in texture, and cost and time constraints must all be carefully considered when using this freeze drying method alone.
Applications of Freeze Drying for Chlorophyll-rich Products
Freeze drying is a versatile preservation technique that can be used for a wide range of chlorophyll-rich products. Here are some examples of applications of freeze drying methods for chlorophyll-rich products:
Vegetables and Fruits
Freeze drying can be used to preserve vegetables and fruits that are high in chlorophyll, such as spinach, kale, broccoli, and green beans. The freeze-dried vegetables and fruits can be used in a variety of applications, such as soups, smoothies, and snacks. Freeze-dried fruits can also be used as a topping for yogurt or cereal.
Herbs
Herbs are another type of product that can benefit from freeze drying. Many herbs are rich in chlorophyll, such as parsley, cilantro, and basil. Freeze drying can preserve the flavor, aroma, and nutrient content of these herbs, making them ideal for use in seasoning blends, sauces, and marinades.
Tea
Green tea and other herbal teas are rich in chlorophyll and other nutrients. Freeze drying can preserve the flavor and nutrient content of these teas, making them ideal for use in green tea, blends, supplements, and other applications.
Algae
Certain types of algae, such as spirulina and chlorella, are rich in chlorophyll and other nutrients. Freeze drying can preserve the nutrient content of these algae, making them ideal for use in supplements, protein powders, and other health products.
Pet Food
Freeze drying can also be used to preserve chlorophyll-rich ingredients in pet food. Many pet owners are interested in feeding their pets a natural, nutrient-rich diet, and freeze-dried pet food can meet this need. Chlorophyll-rich ingredients such as spinach, kale, and spirulina can be incorporated into freeze-dried pet food to provide essential nutrients for pets.
Alternative Methods for Chlorophyll Preservation
Freeze-drying is one of the most effective methods of preserving chlorophyll in food products. However, there are alternative methods that can also be used for preserving chlorophyll, using drying treatments such as refrigeration, blanching, and high-pressure processing.
Refrigeration is a common method of preserving fresh produce, which slows down the enzymatic activity that causes degradation of chlorophyll. However, refrigeration alone is not effective in preserving chlorophyll in fresh sample over the long term, and the produce will eventually spoil.
Blanching is another method of preserving chlorophyll that involves briefly immersing the produce in boiling water, then immediately cooling it down in ice water. This method can help to preserve the green color of the produce, but it can also cause some loss of nutrients and flavor.
High-pressure processing (HPP) is a non-thermal method of food preservation that uses high pressure to inactivate microorganisms and enzymes in food products. This method can help to preserve chlorophyll and other nutrients in food products, while also maintaining the fresh flavor and texture of the produce.
Another alternative method for preserving chlorophyll is the use of natural antioxidants, such as vitamin C and E, which can help to prevent oxidation and degradation of chlorophyll in food products.
In addition to these methods, there are also some emerging technologies that show promise for preserving chlorophyll in food products, such as pulsed electric field processing and ultraviolet light treatment.
Pulsed electric field processing involves applying short pulses of high-voltage electricity to the produce, which can help to inactivate enzymes and preserve the nutrients and green color of the produce. Ultraviolet light treatment involves exposing the produce to ultraviolet light, which can help to stimulate chlorophyll production and improve the overall quality and shelf life of the produce.
Overall, while freeze-drying is one of the most effective methods of preserving chlorophyll in food products, there are alternative methods that can also be used to preserve chlorophyll and other nutrients in food products. The choice of method will depend on the specific food product, as well as factors such as cost, availability, and processing time.
What are the benefits of using a freeze dryer for preserving food products compared to other preservation methods?
Freeze-drying is a beneficial method for preserving food products compared to other preservation methods due to several reasons. It is known to retain the nutrient content and flavor of the product, while simultaneously preventing the growth of microorganisms. Freeze-drying is also known to extend the shelf life of the product, making it ideal for long-term storage.

It helps to maintain the color and texture of the food product, making it an ideal preservation method for products with high chlorophyll content. Overall, freeze-drying provides a convenient and effective way to preserve food products while maintaining their quality.
How does hot air drying affect the preservation of chlorophyll in food products?
Hot air drying can have a negative impact on the preservation of chlorophyll in food products. The high temperatures used in hot air drying can cause the degradation of chlorophyll, resulting in the loss of the green color and nutritional value of the product.
Hot air drying can lead to the formation of off-flavors and textures in the food product. Compared to freeze-drying, hot air drying is not an ideal preservation method for products with high chlorophyll content, as it can significantly reduce the quality and nutritional value of the product.
How does freeze drying affect chlorophyll in plants?
Freeze-drying removes water from plants, which can cause changes to the plant’s structure and may result in the loss of some of its pigments, including chlorophyll. However, the extent of chlorophyll loss depends on various factors, such as the type of plant, the freeze-drying conditions, and the duration of the freezing process itself.
Can chlorophyll be preserved using other methods besides freeze-drying?
Yes, chlorophyll can be preserved using other methods besides freeze dryer can, such desirable drying methods such as air-drying, dehydrating in a food dehydrator, or freezing. These methods can help to retain some of the plant’s pigments absorb moisture and nutrients but may not be as effective at preserving the material’s texture and flavor as freeze-drying.
How to Freeze Dry Kale
FAQs
Is chlorophyll important for plants?
Yes, chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy that can be used for growth and survival. Chlorophyll also plays a role in plant metabolism and can help protect the plant from environmental stresses.
Does the loss of chlorophyll during freeze-drying affect the nutritional value of the plant?
The loss of chlorophyll during freeze-drying may cause some loss of nutrients, but it depends on the specific plant and the extent of chlorophyll loss. In general, freeze-drying is an effective method for preserving the nutritional value of food, as it helps to retain many of the vitamins and minerals.
Conclusion
Freeze-drying is an effective method for preserving chlorophyll content in foods. It does not remove chlorophyll, and in fact, it can retain the green color and nutrient content of the food product. However, other factors such as temperature, pre-treatment, and storage conditions can also affect the preservation of chlorophyll in freeze-dried foods. Therefore, proper processing and the storage temperatures and conditions must be maintained to ensure the preservation of chlorophyll and other nutrients in food products.