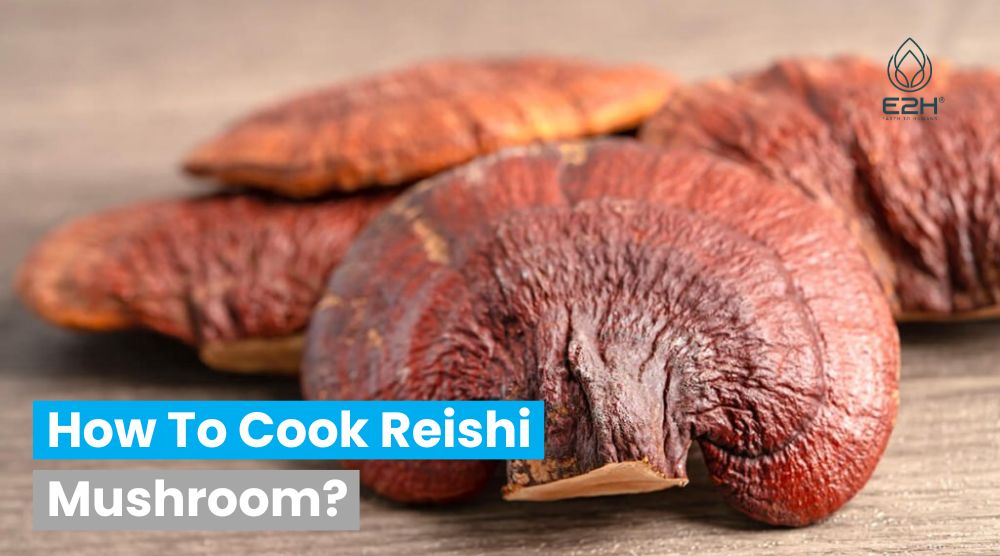
How To Grow Reishi Mushrooms: To grow Reishi mushrooms, prepare a hardwood sawdust substrate, inoculate with Reishi grain spawn, maintain a temperature of 70-80°F, ensure high humidity, and provide indirect light. Harvest when mature, typically in antler or fan shape.
What are the basic requirements for growing Reishi mushrooms?
Basic Requirements for Growing Reishi Mushrooms:
- Substrate: Reishi mushrooms prefer a substrate made of hardwood sawdust, often supplemented with wheat bran. This provides the necessary nutrients for the reishi mycelium to thrive.
- Spawn: Reishi grain spawn or sawdust spawn is essential to introduce the mushroom culture to the substrate. This spawn contains the initial reishi mycelium that will colonize the substrate.
- Environmental Conditions: Reishi mushrooms require specific conditions to grow. They thrive in a fresh air environment with high humidity. The temperature should be maintained between 70-80°F (21-27°C) for optimal growth.
- Equipment: Mushroom grow bags or jars with a filter patch allow for gas exchange while preventing contaminants. Additionally, a mini greenhouse can help maintain humidity.
- Growth Form: Depending on the conditions, Reishi can grow in various forms, such as antler reishi or as a shelf fungus. Proper conditions can promote the desired growth form.
- Harvesting: Once the fruiting bodies or reishi antlers are mature, they can be harvested. Mature mushrooms will often release brown spores, indicating they’re ready.
- Medicinal Properties: Reishi mushrooms are renowned for their medicinal properties. They contain medicinal compounds beneficial for health, making the cultivation process even more rewarding.
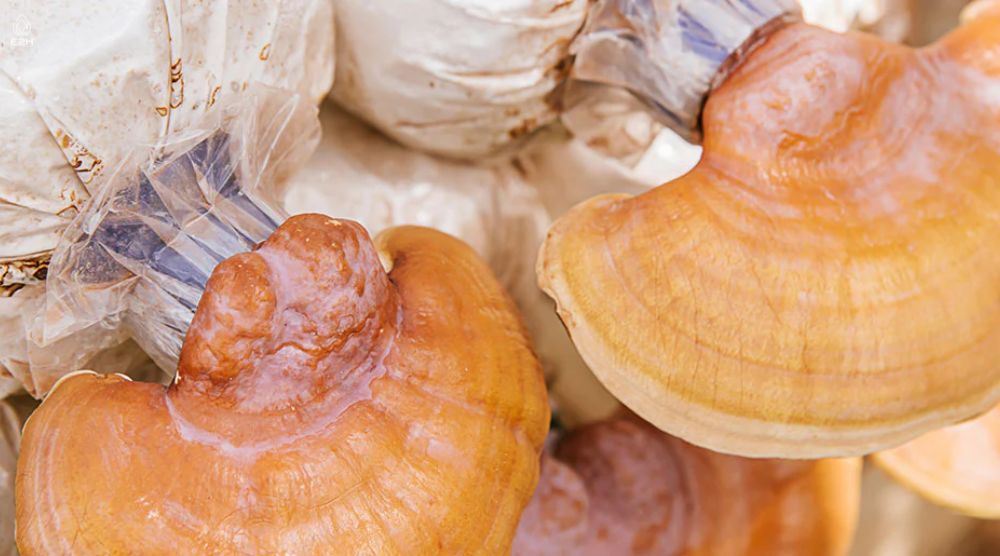

How long does it take to grow Reishi mushrooms from start to harvest?
Growing Reishi mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum) from start to harvest typically takes between 10 to 16 weeks. The initial colonization of the substrate with reishi mycelium can take 4 to 6 weeks. Once fully colonized, the fruiting phase begins, which lasts another 6 to 10 weeks, depending on environmental conditions and the specific strain of Reishi being cultivated. It’s essential to monitor the growth and ensure optimal conditions to achieve a successful harvest within this timeframe.
What type of substrate is best for Reishi mushroom cultivation?
The best substrate for Reishi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum) cultivation is hardwood sawdust, often supplemented with wheat bran or other organic materials. This combination provides the essential nutrients for the Reishi mycelium to flourish.
Hardwood species like oak, alder, or maple are commonly used. Some cultivators also use supplemented hardwood sawdust blocks or pellets.
The substrate’s consistency and nutrient content play a crucial role in supporting the growth and medicinal properties of the Reishi mushroom. Ensuring the substrate is properly sterilized before inoculation is also vital to prevent contamination and promote healthy mushroom growth.
Are there any specific environmental conditions needed for Reishi growth?
Reishi mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum) thrive in specific environmental conditions to ensure optimal growth and medicinal properties. Key conditions include:
- Temperature: A consistent range of 70-80°F (21-27°C) is ideal.
- Humidity: High humidity levels, typically around 90-95%, are crucial for Reishi mushroom growth.
- Air Exchange: Fresh air exchange is essential to prevent carbon dioxide buildup and promote healthy mycelium growth.
- Light: While Reishi doesn’t require much light, a few hours of indirect light daily can be beneficial.
- Protection: A mini greenhouse or grow tent can help maintain these conditions, especially humidity and temperature.
How do I inoculate the substrate with Reishi spawn?
Inoculating the substrate with Reishi spawn is a critical step in the cultivation process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Preparation: Ensure the substrate, typically hardwood sawdust supplemented with wheat bran, is moistened and sterilized.
- Cooling: Allow the sterilized substrate to cool to room temperature.
- Adding Spawn: Break apart the Reishi grain spawn or sawdust spawn and evenly mix it with the substrate.
- Packing: Transfer the inoculated substrate into mushroom grow bags or jars with filter patches for gas exchange.
- Sealing: Seal the bags or jars to prevent contamination.
- Incubation: Place the inoculated bags in a dark, warm area (70-80°F or 21-27°C) for the mycelium to colonize the substrate.
What are the potential challenges or problems I might face while growing Reishi?
Growing Reishi mushrooms, like any cultivation process, comes with its set of challenges:
- Contamination: One of the most common issues is contamination by other fungi or bacteria. This can be due to unsterilized equipment or substrate.
- Improper Humidity: Reishi requires high humidity for growth. Too low or too high can hinder its development.
- Inadequate Air Exchange: Stagnant air can lead to carbon dioxide buildup, affecting the Reishi mycelium growth.
- Suboptimal Temperature: Deviating from the ideal temperature range of 70-80°F (21-27°C) can slow down growth.
- Uneven Growth: This can result from uneven distribution of Reishi spawn in the substrate.
How do I identify and deal with contaminants or diseases in Reishi cultivation?
dentifying and managing contaminants is crucial for successful Reishi cultivation:
- Visual Inspection: Contaminants often manifest as unusual colors (green, black, or pink molds) or off-putting smells.
- Isolation: If contamination is detected in a grow bag or jar, it’s essential to remove and dispose of it immediately to prevent its spread.
- Sterilization: Ensure all equipment, substrates, and workspaces are thoroughly sterilized before and after use.
- Air Filtration: Using a HEPA filter can help reduce airborne contaminants.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly inspect the Reishi mycelium for signs of diseases or pests. If detected, natural fungicides or insecticides can be used.
- Hygiene: Always wash hands and wear clean gloves when handling the substrate or Reishi mushrooms.
How do I harvest Reishi mushrooms once they’re fully grown?
Harvesting Reishi mushrooms is a meticulous process that requires keen observation. When the edges of the Reishi conks or antlers begin to turn upwards and the mushroom’s underside starts releasing brown spores, it’s an indication that they are ready for harvest.
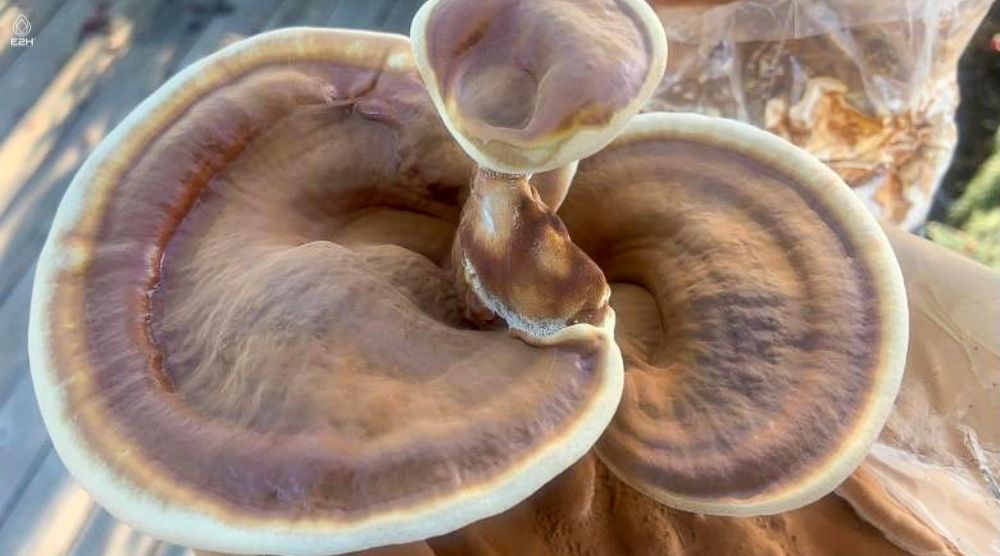
Using a sharp knife or scissors, cut the Reishi mushroom at its base, ensuring not to damage the substrate or any neighboring mushrooms. After harvesting, it’s essential to clean the Reishi by brushing off any substrate remnants. For medicinal use, many cultivators prefer to dry the harvested Reishi, enhancing its shelf life and medicinal properties.
Can I grow Reishi mushrooms indoors, and if so, how?
Yes, Reishi mushrooms can be cultivated indoors, offering better control over environmental conditions. To grow Reishi mushrooms indoors, start by preparing a substrate, typically hardwood sawdust supplemented with wheat bran.
Once sterilized and cooled, inoculate the substrate with Reishi grain spawn. Transfer the inoculated substrate to mushroom grow bags or jars with filter patches for gas exchange. Place these bags in a designated grow area, like a mini greenhouse or grow tent, maintaining a temperature of 70-80°F (21-27°C) and high humidity levels.
Ensure regular fresh air exchange to prevent carbon dioxide buildup. Over time, the Reishi mycelium will colonize the substrate, and fruiting bodies will form. With proper care, indoor cultivation can yield high-quality Reishi mushrooms with potent medicinal compounds.
Are there any specific varieties or strains of Reishi mushrooms that are easier to cultivate?
Reishi mushrooms have several strains and varieties. Among them, the red Reishi is the most popular and widely cultivated due to its recognized medicinal properties and ease of growth.
Other varieties like black, purple, green, white, and yellow Reishi also exist, but their cultivation might differ slightly. The red Reishi strain is particularly adaptable to a variety of substrates, including hardwood sawdust and supplemented grain spawn, making it a preferred choice for both novice and experienced cultivators.
Choosing a strain that’s well-suited to your region’s climate and conditions can further simplify the cultivation process.
How can I turn Reishi mushroom cultivation into a profitable business?
Turning Reishi mushroom cultivation into a profitable business requires a blend of expertise, market research, and strategic planning. Start by understanding the demand for Reishi in your region, given its medicinal benefits.
Investing in quality equipment and substrates ensures a consistent yield of high-quality mushrooms. Offering value-added products like dried Reishi, Reishi powder, or liquide extract can increase profitability. Additionally, educating potential customers about Reishi’s health benefits can drive demand. Collaborating with herbalists, naturopaths, or health stores can open up distribution channels.
Attending workshops or courses on mushroom cultivation can enhance your expertise. Lastly, maintaining sustainable and organic cultivation practices can give your business an edge in the market, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Are there any online courses or workshops on Reishi mushroom cultivation?
Yes, with the rising interest in medicinal mushrooms and theircultivation, several online platforms offer courses and workshops on Reishi mushroom cultivation. These courses often cover the entire cultivation process, from substrate preparation to harvesting.
Websites like Udemy, Coursera, and specialized mushroom cultivation forums often host such courses. Additionally, mushroom cultivation enthusiasts and experts frequently conduct webinars and workshops, providing hands-on experience and insights into best practices. Joining mycology communities online can also provide recommendations and reviews on the best courses available.
How is reishi mycelium different from other mushrooms in its look and growth?
Reishi mycelium is distinct in both appearance and growth pattern. Unlike some other mushroom mycelium that appears fluffy and white, Reishi mycelium often has a denser, matted texture with a slightly off-white to beige color. Its growth is more aggressive, quickly colonizing the substrate.
As it matures, the mycelium might exhibit a glossy sheen, indicative of the mushroom’s natural protective compounds. This unique growth pattern and appearance are adaptations of Reishi, making it resilient and suited for various cultivation environments, especially on hardwood substrates.
Why do we call Reishi mushroom “Ganoderma lucidum”?
“Ganoderma lucidum” is the scientific name for the Reishi mushroom. In taxonomic nomenclature, every organism is given a Latinized name to standardize identification across regions and languages. “Ganoderma” translates to “shiny skin,” referring to the mushroom’s glossy appearance, while “lucidum” means “bright” or “shiny,” emphasizing its polished, varnished look.
This name not only helps in the scientific classification but also highlights the mushroom’s unique characteristics. Using the scientific name ensures clarity, especially since common names like “Reishi” can vary across cultures and regions.
How are Reishi mushrooms’ health benefits different from other mushrooms?
Reishi mushrooms, known as Ganoderma lucidum scientifically, are renowned for their potent medicinal properties. While many mushrooms offer health benefits, Reishi stands out for its immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. It’s also known to support liver function, reduce blood pressure, and alleviate allergies.
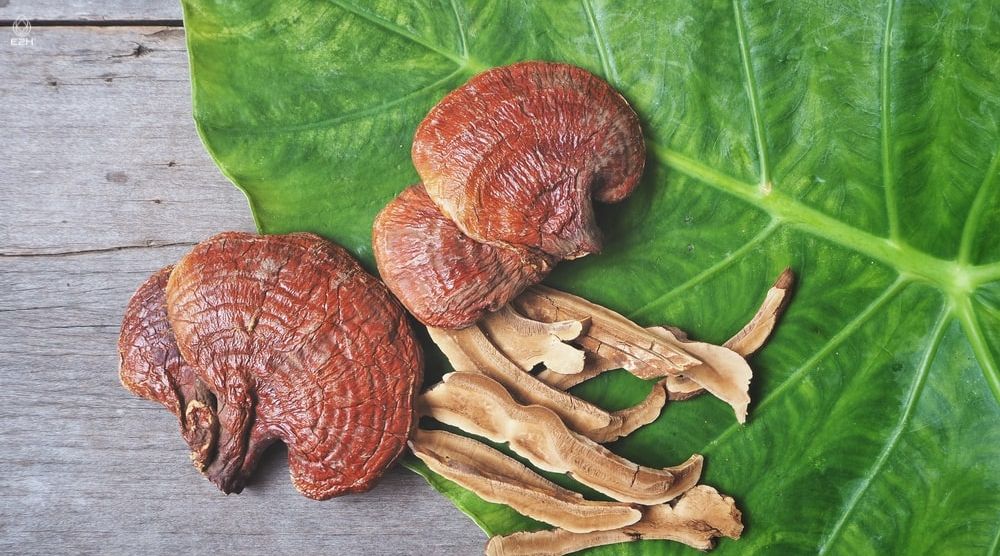

The presence of unique compounds like triterpenoids, polysaccharides, and peptidoglycans in Reishi distinguishes its health benefits from other mushrooms. While other mushrooms might aid digestion or provide essential nutrients, Reishi’s benefits are more holistic, targeting overall well-being and longevity.
Why is reishi grain spawn important for growing them?
Reishi grain spawn serves as the initial inoculum to introduce the Reishi mycelium to the substrate. It’s a mixture of grains, like rye or millet, colonized by Reishi mycelium. Using grain spawn ensures a faster and more uniform colonization of the substrate, providing a solid foundation for the mushrooms to fruit.
The nutrients in the grain also give an initial boost to the mycelium, promoting vigorous growth. Without this spawn, establishing Reishi in the substrate would be challenging and less efficient.
How do you get sawdust ready for growing Reishi?
Preparing sawdust for Reishi cultivation involves a few steps. First, choose a hardwood sawdust, preferably from oak, maple, or alder. Mix the sawdust with supplements like wheat bran to enhance its nutritional content.
Moisten the mixture to achieve a field capacity, where it’s damp but not dripping wet. The next crucial step is sterilization.
Pack the moistened sawdust into mushroom grow bags or jars and sterilize them, typically using a pressure cooker or autoclave, to eliminate any potential contaminants. Once cooled, the sterilized sawdust is ready for inoculation with Reishi grain spawn.
What makes antler reishi look different from regular Reishi?
Antler reishi is a unique growth form of the Reishi mushroom. Unlike the typical fan or shelf-shaped Reishi, antler reishi grows elongated, resembling deer antlers. This form usually occurs when there’s limited fresh air exchange, causing the mushroom to grow upwards seeking oxygen.
Antler reishi lacks the broad cap seen in regular Reishi and instead has a more cylindrical shape. While both forms have similar medicinal properties, the antler form is often considered more potent due to a higher concentration of beneficial compounds.
FAQs For ‘How To Grow Reishi Mushrooms’
What’s the ideal temperature for Reishi mushroom cultivation?
Reishi mushrooms thrive at temperatures between 70-80°F (21-27°C) for optimal growth.
Can Reishi mushrooms be grown on materials other than hardwood sawdust?
Yes, Reishi can also grow on grains, logs, and supplemented substrates, but hardwood sawdust yields the best results.
How often should I water the Reishi substrate?
Maintain consistent moisture; misting daily is ideal, but avoid over-saturating the substrate.
Do Reishi mushrooms need light to grow?
While not essential, a few hours of indirect light daily can benefit Reishi growth.
How can I increase the medicinal potency of my Reishi mushrooms?
Ensure optimal growing conditions, and consider harvesting during the antler stage for increased medicinal compounds.
Conclusion
Growing Reishi mushrooms is a rewarding endeavor, both for their medicinal properties and the joy of cultivation. With the right knowledge, substrate, and environmental conditions, anyone can cultivate these beneficial fungi successfully. As interest in natural health solutions continues to rise, understanding the process of Reishi cultivation becomes even more valuable. So, as you explore the world of mushroom cultivation, let Reishi be a shining example of nature’s wonders at its best.












