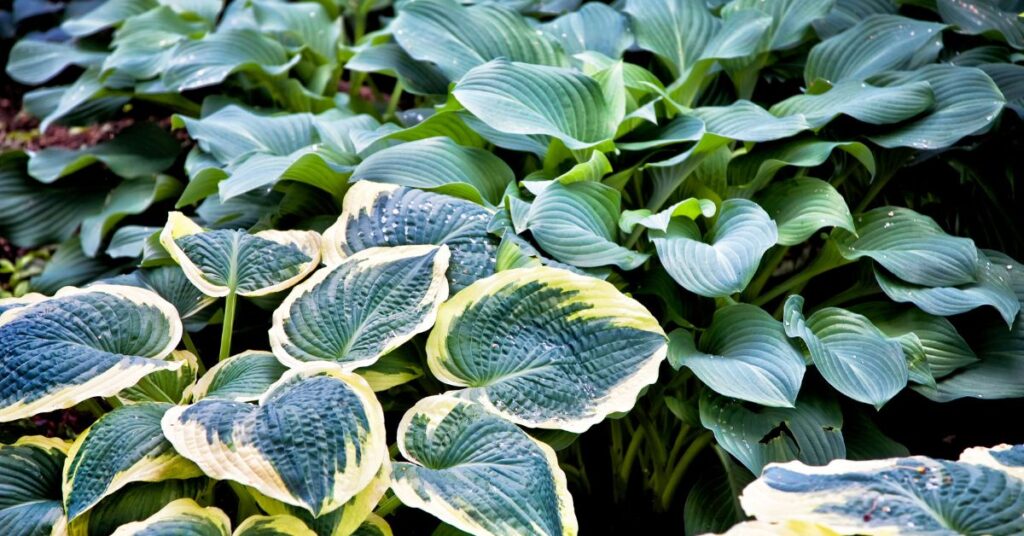
Do Shade Plants Have More Chlorophyll: Yes, shade plants have more chlorophyll than plants that grow in direct sunlight. This is why shade leaf, because they have adapted to low light conditions by developing more chlorophyll.
What are shade plants?
Shade plants are plants that are adapted to growing in low light conditions. These plants grow in areas that receive less than six hours of direct sunlight per day. Shade plants have adapted to low light conditions by developing larger leaves, thinner leaves, and more chlorophyll. Some examples of shade plants include ferns, hostas, and impatiens.
What is chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is a pigment present in the chloroplasts of plant cells. It absorbs light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of plants and is essential for the survival of plants.
Do shade plants have more chlorophyll?
Shade plants have more chlorophyll than plants that grow in direct sunlight. This is because they have adapted to low light conditions by developing more chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a pigment that is essential for the survival of plants, as it helps them absorb light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis.
In low light conditions, shade plants need to be more efficient at capturing and utilizing available light energy. One way they do this is by producing more chlorophyll, which allows them to absorb more light and convert it into energy. Shade plants also tend to have larger leaves, which provides a larger surface area for the absorption of light.

In contrast, plants that grow in direct sunlight or intense sun may have less chlorophyll and smaller leaves to reduce water loss through transpiration. The excess light and heat can damage their leaves, so they need to have other mechanisms to cope with these conditions.
Overall, shade plants have adapted to low light conditions by producing more chlorophyll and developing larger leaves, which help them absorb and utilize available light energy more efficiently.
Why do shade plants have more chlorophyll?
Shade plants have more chlorophyll to compensate for the lack of available light. In low light conditions, shade plants need to be more efficient at capturing and utilizing available light energy. Chlorophyll is essential for the absorption of light energy and the process of photosynthesis.
Therefore, shade plants produce more chlorophyll to increase their ability to capture available light and convert it into chemical energy. This adaptation allows shade plants to survive and thrive in low light conditions, where plants that rely on direct sunlight may struggle. The increased chlorophyll content also contributes to the darker green color of shade plants compared to their full sun-exposed counterparts.
What effect does shade have on chlorophyll content?
Shade has a significant effect on chlorophyll content in plants. In low light conditions, such as those found in shade, plants produce more chlorophyll to compensate for the reduced amount of available light energy. This adaptation allows plants to absorb and convert available light energy more efficiently.
Shade plants typically have a darker green color than their sun-exposed counterparts, which is a result of their increased chlorophyll content. Conversely, plants that receive direct sunlight may produce lighter green and less chlorophyll to reduce the risk of photodamage and water loss. Overall, the chlorophyll content of plants is highly influenced by the intensity and quality of light they receive.
Do shade plants have more chlorophyll a or B?
Shade plants tend to have higher levels of both chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b compared to plants that grow in direct sunlight. This is because these pigments are essential for photosynthesis and shade plants need to have both sun be more efficient at capturing available light energy. While the ratio of chlorophyll a to chlorophyll b can vary between plant species and environmental conditions, shade plants typically have a higher total amount of both pigments to maximize their ability to absorb and convert available light energy.

How does chlorophyll help plants?
Chlorophyll is a vital pigment in plants that is responsible for absorbing light energy and initiating the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll molecules capture light energy and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
This process provides plants with the energy and nutrients they need to grow and reproduce. Chlorophyll also plays a role in protecting plants from the harmful effects of excess light energy by absorbing and dissipating excess light energy as heat. In addition, the green color of chlorophyll gives plants their characteristic appearance and enables them to blend in with their surroundings.
Can plants have too much chlorophyll?
Yes, plants can have too much light saturation point much chlorophyll. When plants receive excess light energy, they may produce an excessive amount of chlorophyll, which can lead to photodamage and oxidative stress. Additionally, high levels of chlorophyll can reduce a plant’s ability to regulate water loss, leading to dehydration. Therefore, while chlorophyll is essential for plant growth and survival, excessive amounts can be harmful and lead to negative impacts on plant health and development.
Which plant has more chlorophyll?
The amount of chlorophyll in a plant can vary depending on a number of factors, including the characteristics of the plant species, environmental conditions, and the stage of growth. Generally, shade plants tend to have higher levels of chlorophyll compared to plants that grow in direct sunlight, as they need to be more efficient at capturing available light energy. However, the exact amount of chlorophyll can vary greatly between plant species and individual plants within a species.
How do sun leaves tend to differ in color from shade leaves?
Sun leaves tend to be a lighter shade of green compared to shade leaves, which are darker and more vibrant in color. This difference in color is due to the amount of chlorophyll present in each type of leaf. Shade leaves contain more chlorophyll because they need to be more efficient at capturing the limited amount of light available in shaded areas.

Sun leaves, on the other hand, have less chlorophyll because they are exposed to direct sunlight and need to protect themselves from excess light energy. In some cases, sun leaves may also contain pigments like anthocyanins that give them a reddish or purplish tint red light show.
How does shoot growth vary in response to changes in light energy?
Shoot growth varies in response to changes in light energy due to the process of phototropism, where plants grow towards sources of light. In low light conditions, shoots grow taller and thinner in order to reach more light. They do this by elongating their internodes, the parts of the stem between leaves, which results in a longer stem.
In contrast, in high light conditions, shoots grow shorter and thicker to protect themselves from excessive light energy. The shorter and thicker stems result from shorter internodes and thicker cell walls. These growth responses allow plants to optimize their use of available light energy and regulate their exposure to potential photodamage.
Do plants have more chlorophyll A or B?
FAQs
Can shade plants survive in direct sunlight?
Some shade plants can survive in direct sunlight, but they may not grow as well sun and shade as they would in low light conditions. Shade plants are adapted to growing in low light conditions, and direct sunlight can cause them to become stressed and damaged.
Do all plants have the same amount of chlorophyll?
No, not all plants have the same amount of chlorophyll. Plants that grow in low light conditions, such as trees or as shade plants, tend to have more chlorophyll than plants that grow in direct sunlight.
How can I tell if my plants have chlorosis?
Plants with chlorosis will have yellowing leaves. The veins of the leaves may remain green, while the rest of leaf surface of the leaf turns yellow. Chlorosis can be caused by a lack of nutrients, poor soil conditions, or a genetic defect.
Conclusion
Shade plants are adapted to growing in low light conditions sun and shade leaves are believed to have more chlorophyll than plants that grow in direct sunlight. Chlorophyll is essential for the survival of plants and helps them absorb light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. However, it is important to maintain the proper balance of chlorophyll in plants to ensure their health and vitality.